ステッピング・モーター

ステッピング・モーター
低速時や静止状態での高トルクで人気があるステッピング・モーターは、高精度の位置決めが必要な場合に選択されるデバイスです。アナログ・デバイセズのTrinamicの業界最先端技術と組み合わせることで、ステッピング・モーターの特性を活用し、これらのモーターは、1回転あたり最大51,200マイクロ・ステップを用いてデジタル情報を完璧な物理的動作に変換します。
低速時や静止状態での高トルクで人気があるステッピング・モーターは、高精度の位置決めが必要な場合に選択されるデバイスです。アナログ・デバイセズのTrinamicの業界最先端技術と組み合わせることで、ステッピング・モーターの特性を活用し、これらのモーターは、1回転あたり最大51,200マイクロ・ステップを用いてデジタル情報を完璧な物理的動作に変換します。
滑らかで高精度な動作のためのマイクロ・ステッピング
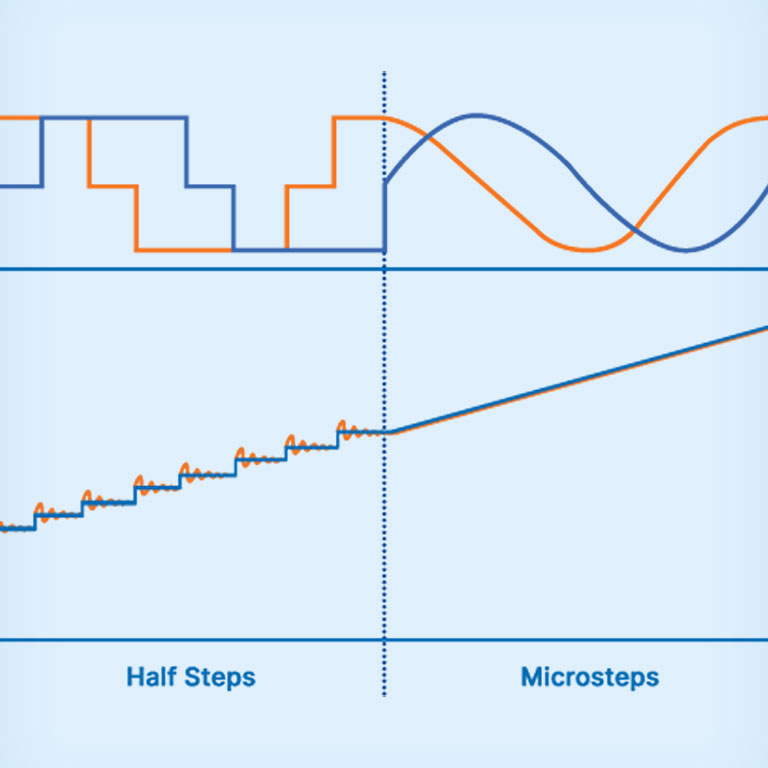
ステッピング・モーターは通常、永久磁石のローターと、ステータとして機能するモーター・コイルを使用します。モーター・コイルに電流を流すことで電磁界が生成され、磁気ローターを所定の位置に強制的に移動させます。一般的なハイブリッド・ステッピング・モーターは50組の磁極対を持ち、これによりモーターはフル・ステップが200に近づきます。つまり、360°の完全な回転あたり200の位置決めが可能になります。ただし、ハーフ・ステップやマイクロ・ステップのようなより小さなステップは、追加の電流状態を用いて生成することができます。これにより、モーターの精度、トルク、効率が向上し、ステップ・ロス、振動、騒音が低減されます。

滑らかで高精度な動作のためのマイクロ・ステッピング
ステッピング・モーターは通常、永久磁石のローターと、ステータとして機能するモーター・コイルを使用します。モーター・コイルに電流を流すことで電磁界が生成され、磁気ローターを所定の位置に強制的に移動させます。一般的なハイブリッド・ステッピング・モーターは50組の磁極対を持ち、これによりモーターはフル・ステップが200に近づきます。つまり、360°の完全な回転あたり200の位置決めが可能になります。ただし、ハーフ・ステップやマイクロ・ステップのようなより小さなステップは、追加の電流状態を用いて生成することができます。これにより、モーターの精度、トルク、効率が向上し、ステップ・ロス、振動、騒音が低減されます。
{{modalTitle}}
{{modalDescription}}
{{dropdownTitle}}
- {{defaultSelectedText}} {{#each projectNames}}
- {{name}} {{/each}} {{#if newProjectText}}
-
{{newProjectText}}
{{/if}}
{{newProjectTitle}}
{{projectNameErrorText}}