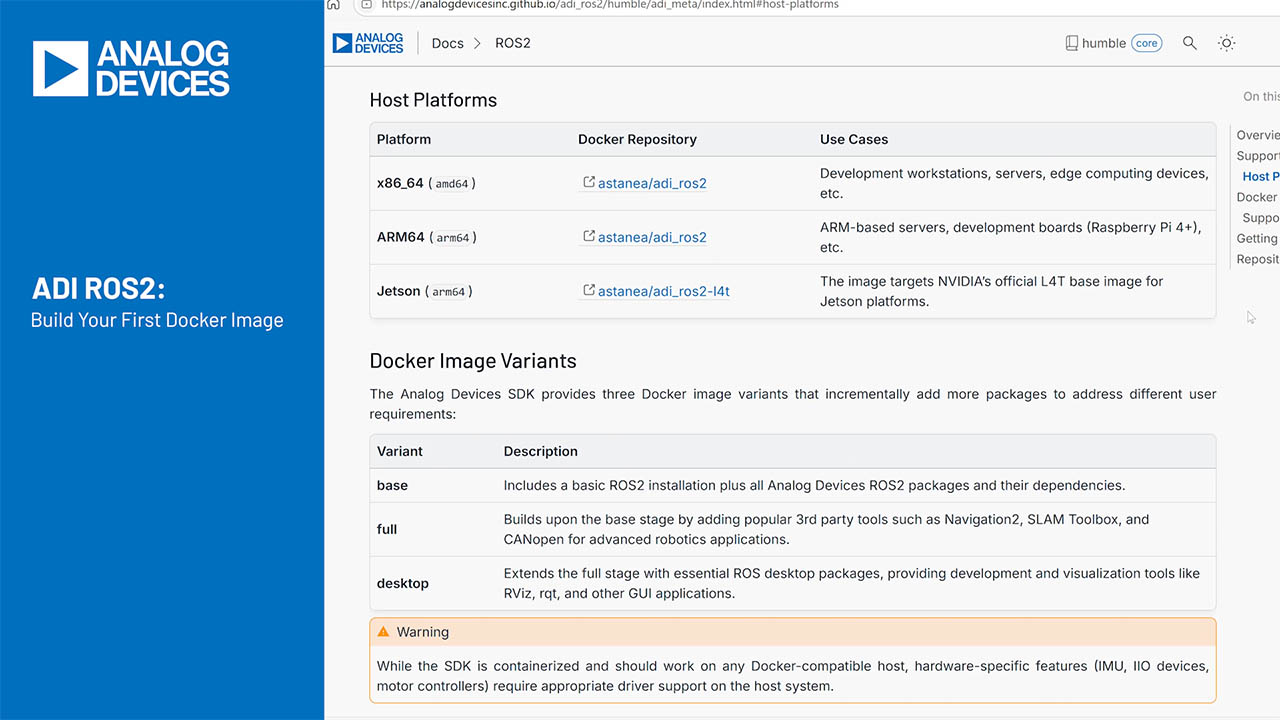
Abstract
This application note presents the two main types of blood pressure monitors, various measurement techniques, the functions of electrical components, and some crucial aspects that designers must consider when selecting products.
Overview
A blood pressure monitor, or sphygmomanometer, uses an inflatable air-bladder cuff and a listening device or pressure sensor to measure blood pressure in an artery. This monitoring can be performed by using either of two methods: a manually inflated cuff with a stethoscope for listening to arterial wall sounds (the auscultatory method), or a blood pressure monitor that contains a pressure sensor for sensing arterial wall vibrations (the oscillometric method).

Upper-arm blood pressure monitor.

Wrist blood pressure monitor.
Automatic Monitor Types
The two main types of automatic blood pressure monitors are upper-arm and wrist models. The upper-arm model has a cuff that is placed on the upper arm; the cuff is connected by a tube to the monitor that rests on a surface near the arm. The wrist model is smaller and the entire unit wraps around the wrist—this is a much more space-critical design. Some upper-arm models require manual inflation of the cuff, but most upper-arm and all wrist models are fully automatic.
Measurement Techniques
An automatic blood pressure monitor inflates a cuff surrounding an arm with sufficient pressure to prevent blood flow in the local main artery. This pressure is gradually released until the moment that the blood begins to flow through the artery, the measurement of which determines the systolic pressure. Pulse rate is also sensed at this time. The measurement taken when the blood flow is no longer restricted determines the diastolic pressure. This complete measurement cycle is performed automatically with a pump, cuff, valve, and pressure sensor.
The signal from the pressure sensor is conditioned with an op-amp circuit or by an instrumentation amplifier before data conversion by an analog-to-digital converter (ADC). The systolic pressure, diastolic pressure, and pulse rate are then calculated in the digital domain using a method appropriate for the type of monitor and sensor utilized. The resulting systolic, diastolic, and pulse-rate measurements are displayed on a liquid-crystal display (LCD), time/date-stamped, and stored in nonvolatile memory.

Functional block diagram of a blood pressure monitor that includes an advanced voice indicator.
Data Interface
Some blood pressure monitors have the ability to upload data to a computer for further analysis and tracking of measurements over time. This data transfer is usually done through a USB interface. A discrete USB transceiver can provide this functionality, or it can be integrated within the microcontroller.
Audio Indicators
Audible indicators in blood pressure monitors range from simple beepers to more advanced audio output. A simple beeper can be driven by one or two microcontroller port pins that have pulse-width modulation (PWM) capability. More advanced voice indicators can be achieved by adding an audio digital-to-analog converter (DAC) and speaker amplifier.
Power Management
Upper-arm monitors typically use four AAA (1.5V) alkaline batteries and wrist monitors typically use two AAA alkaline batteries. The monitor's pump and analog circuitry require a 5V or 3.3V supply and the digital circuitry needs a 3.3V or 1.8V supply, depending on the technology used. Consequently, a typical upper-arm monitor would need a buck-boost switching regulator to regulate the pump/analog supply voltage to 5V and a low-dropout linear regulator (LDO) for the 3.3V digital requirement. The typical wrist monitor would use a boost switching regulator to step up the pump/analog supply voltage to 3.3V and an LDO for the 1.8V digital supply.
To extend battery life, powering down the switching regulators may be possible while the monitor is off, as long as the real-time clock (RTC) keeps running and the monitor can easily be turned back on.
Display and Backlighting
Blood pressure monitors use a simple LCD with 100 segments or less that can be driven by a driver integrated within the microcontroller. Backlighting can be added by using 1 or 2 white LEDs (WLEDs) or an electroluminescent (EL) source. A discrete WLED driver can easily be added to a monitor design by using a switching topology for wrist monitors and a linear topology for upper-arm monitors.
Electrostatic Discharge
All monitors must pass IEC 61000-4-2 electrostatic discharge (ESD) requirements. Using circuitry with built-in ESD protection or adding ESD line protectors to exposed traces can help meet these requirements.
Related to this Article
Products
Low-Dropout, Constant-Current Triple White LED Bias Supply
White LED Step-Up Converter in SOT23
180mA, 1x/2x, White LED Charge Pump in 3mm x 3mm TDFN
2.7V to 3.6V and 4.5V to 5.5V, Low-Power, 4-/8-/12-Channel, 2-Wire Serial 8-Bit ADCs
12-Bit 300ksps ADCs with FIFO, Temp Sensor, Internal Reference
12-Bit 300ksps ADCs with FIFO, Temp Sensor, Internal Reference
16-Bit, Low-Power, 2-Channel, Sigma-Delta ADCs
16-Bit, +5V, 200ksps ADC with 10µA Shutdown
2.7V to 3.6V and 4.5V to 5.5V, Low-Power, 4-/8-/12-Channel, 2-Wire Serial 8-Bit ADCs
12-Bit 300ksps ADCs with FIFO, Temp Sensor, Internal Reference
16-Bit, Low-Power, 2-Channel, Sigma-Delta ADCs
I²C, 32-Bit Binary Counter Watchdog Clock
16-Bit Microcontrollers with Infrared Module and Optional USB
Low-Power LCD Microcontroller
16-Bit Microcontroller with Infrared Module
High PSRR, Low-Dropout, 150mA Linear Regulators
High PSRR, Low-Dropout, 150mA Linear Regulators