要約
DS2482は、I2Cから1-Wireへのブリッジです。DS2482によって、I2C通信を備えたあらゆるホストは、正しく計時されスルー制御された1-Wire信号波形を生成することができます。このアプリケーションノートはI2C 1-WireラインドライバDS2482のユーザガイドであり、1-Wireマスタの一般オペレーションのための通信セッションを詳細に説明します。
はじめに
1-Wireネットワークは単一マスタと1つ以上のスレーブデバイスから構成されています。1-Wireマスタは、マイクロプロセッサのIOピンとマニュアル生成タイミングパルスで作成することができます。I2Cから1-WireへのブリッジDS2482によって、設計エンジニアは1-Wireタイミングの詳細を実行する手間が軽減されます。DS2482構成の簡易図については図1を参照してください。このアプリケーションノートでは、DS2482を使用した基本および拡張1-Wireオペレーションの高効率のアプリケーションプログラミングインタフェース(API)の実行を示します。各1-WireオペレーションのI2C通信が説明されています。DS250xシリーズのようなEPROMベースのデバイスのプログラミングを除き、これらのオペレーションは現在およびこれからの1-Wireデバイスの全機能を実行するための方法一式を提供します。この方法で1-Wireオペレーションを要約することで、1-Wireマスタタイプに依存しない1-Wireアプリケーションにつながります。
このアプリケーションノートはDS2482のデータシートを補足するものですが、取って代わるものではありません。DS2482は、シングルチャネル1-Wireマスタ(DS2482-100)、低電力スリープモード付きシングルチャネル1-Wireマスタ(DS2482-101)、および8チャネル1-Wireマスタ(DS2482-800)の3つの構成で入手可能です。
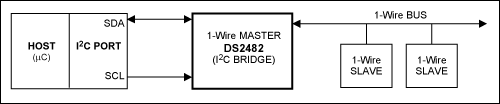
図1. I2C通信および1-WireネットワークのブリッジとしてのDS2482機能の簡易図
1-Wireインタフェース
基本命令と呼ばれる1-Wireの基本機能がいくつかあり、その機能においてはアプリケーションはあらゆる1-Wire通信セッションを実行する必要があります。最初の機能(OWReset)はネットワーク上の1-Wireスレーブをすべてリセットし、1-Wireマスタからのコマンド向けに用意させます。2番目の機能(OWWriteBit)は1-Wireマスタからスレーブにビットを書き込み、3番目の機能(OWReadBit)は1-Wireスレーブからビットを読み込みます。1-Wireマスタは全1-Wireビット通信を開始する必要があるため、「読み込み」はサンプリングした結果を用いてシングルビットを技術的に「書き込む」ことになります。他のほとんどすべての1-Wireオペレーションはこれらの3つのオペレーションからつくることができます。たとえば、1-Wireネットワークに書き込まれたバイトはわずか8つのシングルビットの書き込みです。
これらの同じ3つの基本命令を使用すると、1-Wire検索アルゴリズムを構築することもできます。しかし、DS2482は1-Wireトリプレットと呼ばれる検索ヘルプ機能を内蔵しており、検索に必要な通信オーバヘッドが大幅に低減されます。同様に、8つのシングルビットコマンドを行うよりも効率的なバイト1-Wire通信コマンドがあります。
表1は、3つの基本命令(OWReset、OWWriteBit/OWReadBit、およびOWWriteByte/OWReadByte)に加えて、1-Wireの基本オペレーションの中核セットをともに構成する他の3つの便利な機能(OWBlock、OWSearch、msDelay)を示します。これ以降、このアプリケーションノート全体を通じて、これらのオペレーションの名前を使用します。
| Operation | Description |
| OWReset | Sends the 1-Wire reset stimulus and check for the presence pulse of 1-Wire slave devices. |
| OWWriteBit/OWReadBit | Sends to or receives from the 1-Wire network a single bit of data. |
| OWWriteByte/OWReadByte | Sends to or receives from the 1-Wire network a single byte of data. |
| OWBlock | Sends to and receives from the 1-Wire network multiple bytes of data. |
| OWSearch | Performs the 1-Wire Search Algorithm (see application note 187). |
| msDelay | Delays at least the specified number of milliseconds. Used for timing strong pullup operations. |
多くの1-Wireスレーブデバイスは、標準とオーバドライブの2つの異なる通信速度で動作可能です。すべてのデバイスは標準速度に対応しています。オーバドライブは標準よりも約10倍の速さになります。DS2482は、両方の1-Wire速度に対応しています。
1-Wireデバイスは通常、1-Wireネットワークから、一部またはすべての動作エネルギーを得ます。ただし、デバイスによっては、プロトコルの特定の箇所でさらなる給電を必要とするものもあります。たとえば、温度の変換やセキュアハッシュアルゴリズム(SHA-1)ハッシュの計算を必要とするデバイスがあります。この作業を行うための電力は、1-Wireネットワーク上により大きなストロングプルアップを設けることによって供給されます。この給電中に通常の通信を行うことはできません。DS2482は、Strong Pullup (SPU)フラグをセットして電力を供給します。フラグをセットすることで、1-Wire通信の次のバイト/ビットの後でストロングプルアップが発行されます。DS2482-100およびDS2482-101には、予備である大きな電流によるストロングプルアップを制御する外部ピン(PCTLZ)もあります。
表2は、1-Wireの速度、給電、およびプログラミングパルスについての1-Wireの拡張オペレーションを示しています。
| Operation | Description |
| OWSpeed | Sets the 1-Wire communication speed, either standard or overdrive. Note that this only changes the communication speed of the 1-Wire master; the 1-Wire slave device must be instructed to make the switch when going from normal to overdrive. The 1-Wire slave will always revert to standard speed when it encounters a standard-speed 1-Wire reset. |
| OWLevel | Sets the 1-Wire power level (normal or power delivery). |
| OWReadBitPower | Reads a single bit of data from the 1-Wire network and optionally applies power delivery immediately after the bit is complete. |
| OWWriteBytePower | Sends a single byte of data to the 1-Wire network and applies power delivery immediately after the byte is complete. |
ホストの構成
DS2482のホストにはI2Cの通信ポートが必要です。このアプリケーションノートでは、ホストの設定は網羅されていません。ただし、ホストは、標準インタフェースI2Cのオペレーションを備えている必要があります。これらのI2Cオペレーションの中にはホストインタフェースによってより高レベルの機能にバンドルされていることがあることに注意してください。必要なオペレーションは表3にてご覧いただけます。
| Operation | Description |
| I2C_start | I2C start command. |
| I2C_rep_start | I2C repeated start command. |
| I2C_stop | I2C stop command. |
| I2C_write | Writes a byte to the I2C bus. The byte to write is passed to the function. |
| I2C_read | Reads a byte from the I2C bus. The byte read is returned from the function. |
DS2482の構成
1-Wireオペレーションを試す前に、ホストはDS2482のI2C 1-Wireラインドライバをセットアップして、このドライバと同期をとる必要があります。DS2482と通信するには、スレーブアドレスを知る必要があります。図2に、DS2482-100、DS2482-101、およびDS2482-800のスレーブアドレスを示します。

図2. DS2482のI2Cのスレーブアドレス
DS2482のI2Cコマンド
以下の凡例はDS2482のデータシートから引用したものであり、このデバイスによるI2C通信のシーケンスを表すための簡易表記です。今後、これらの通信シーケンスを繰り返して使用することになるため、ここで追加の説明を行って、1-Wireの基本オペレーションと拡張オペレーションを実装するためのCのサンプルコードを示します。
| Symbol | Description |
| S | START Condition |
| AD, 0 | Select DS2482 for Write Access |
| AD, 1 | Select DS2482 for Read Access |
| Sr | Repeated START Condition |
| P | STOP Condition |
| A | Acknowledged |
| A\ | Not acknowledged |
| (Idle) | Bus not busy |
| <byte> | Transfer of one byte |
| DRST | Command 'Device Reset', F0h |
| WCFG | Command 'Write Configuration', D2h |
| CHSL | Command 'Channel Select', C3h (DS2482-800 only) |
| SRP | Command 'Set Read Pointer', E1h |
| 1WRS | Command '1-Wire Reset', B4h |
| 1WWB | Command '1-Wire Write Byte', A5h |
| 1WRB | Command '1-Wire Read Byte', 96h |
| 1WSB | Command '1-Wire Single Bit', 87h |
| 1WT | Command '1-Wire Triplet', 78h |
データ方向コード
| Master-to-Slave | Slave-to-Master |
このアプリケーションノートの多くの図に見られるデータ方向コードは、マスタからスレーブへの通信(灰色)、またはその逆の、スレーブからマスタへの通信(白)を示します。
DS2482の設定オペレーション
以下のオペレーションはDS2482のセットアップと構成に使用されています。これらのオペレーションのいくつかは1-Wireオペレーションによるサブルーチンと呼ばれています。
DS2482の検出
例1はCの検出および構成シーケンスを示します。DS2482に書き込まれるデフォルト値には、1-Wire速度(標準)、ストロングプルアップ(オフ)、プレゼンスパルスマスキング(オフ)、およびアクティブプルアップ(オン)があります。この状態はグローバル変数で維持されるため、デバイスがこのデフォルト状態にリセットして戻る必要がある場合に復帰させることができます。異なるデフォルト値が異なるアプリケーションによっては適切なことがあります。
// DS2482 state
unsigned char I2C_address;
int c1WS, cSPU, cPPM, cAPU;
int short_detected;
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// DS2428 Detect routine that sets the I2C address and then performs a
// device reset followed by writing the configuration byte to default values:
// 1-Wire speed (c1WS) = standard (0)
// Strong pullup (cSPU) = off (0)
// Presence pulse masking (cPPM) = off (0)
// Active pullup (cAPU) = on (CONFIG_APU = 0x01)
//
// Returns: TRUE if device was detected and written
// FALSE device not detected or failure to write configuration byte
//
int DS2482_detect(unsigned char addr)
{
// set global address
I2C_address = addr;
// reset the DS2482 ON selected address
if (!DS2482_reset())
return FALSE;
// default configuration
c1WS = FALSE;
cSPU = FALSE;
cPPM = FALSE;
cAPU = CONFIG_APU;
// write the default configuration setup
if (!DS2482_write_config(c1WS | cSPU | cPPM | cAPU))
return FALSE;
return TRUE;
}
例1. DS2482の検出
DS2482デバイスのリセット
図3は、DS2482デバイスリセットのI2C通信シーケンスを示します。例2はCのDS2482リセットコマンドシーケンスを示しており、このコマンドシーケンスはデバイスのステートマシンロジックのグローバルリセットを実行し、あらゆる進行中の1-Wire通信を終了します。このデバイスリセットのコマンドコードはF0hです。

図3. パワーアップ後のデバイスリセット。この例には、コマンドの成功を検証するための読出しアクセスがオプションで含まれています。
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Perform a device reset on the DS2482
//
// Returns: TRUE if device was reset
// FALSE device not detected or failure to perform reset
//
int DS2482_reset()
{
unsigned char status;
// Device Reset
// S AD,0 [A] DRST [A] Sr AD,1 [A] [SS] A\ P
// [] indicates from slave
// SS status byte to read to verify state
I2C_start();
I2C_write(I2C_address | I2C_WRITE, EXPECT_ACK);
I2C_write(CMD_DRST, EXPECT_ACK);
I2C_rep_start();
I2C_write(I2C_address | I2C_READ, EXPECT_ACK);
status = I2C_read(NACK);
I2C_stop();
// check for failure due to incorrect read back of status
return ((status & 0xF7) == 0x10);
}
例2. デバイスリセットのコード
DS2482の書き込み構成
図4はDS2482の書き込み構成I2C通信例を示しています。例3はCのDS2482書き込み構成コマンドシーケンスを示しています。書き込み構成のコマンドコードはD2hです。

図4. Write Configurationレジスタ。この例にはコマンドの成功を検証するための読み出しがオプションで含まれています。
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Write the configuration register in the DS2482. The configuration
// options are provided in the lower nibble of the provided config byte.
// The uppper nibble in bitwise inverted when written to the DS2482.
//
// Returns: TRUE: config written and response correct
// FALSE: response incorrect
//
int DS2482_write_config(unsigned char config)
{
unsigned char read_config;
// Write configuration (Case A)
// S AD,0 [A] WCFG [A] CF [A] Sr AD,1 [A] [CF] A\ P
// [] indicates from slave
// CF configuration byte to write
I2C_start();
I2C_write(I2C_address | I2C_WRITE, EXPECT_ACK);
I2C_write(CMD_WCFG, EXPECT_ACK);
I2C_write(config | (~config << 4), EXPECT_ACK);
I2C_rep_start();
I2C_write(I2C_address | I2C_READ, EXPECT_ACK);
read_config = I2C_read(NACK);
I2C_stop();
// check for failure due to incorrect read back
if (config != read_config)
{
// handle error
// ...
DS2482_reset();
return FALSE;
}
return TRUE;
}
例3. DS2482の書き込み構成
DS2482のチャネルセレクト
図5はDS2482-800のチャネルセレクトI2C通信例を示しています。有効チャネルは0~7です。このオペレーションはDS2482-100またはDS2482-101に適用されないことに注意してください。例4はCのDS2482-800チャネルセレクトコマンドシーケンスを示しています。チャネルセレクトのコマンドコードはC3hです。チャネルが選択された後、全1-Wireオペレーションはそのチャネルで実行されます。

図5. Write Channel Selectionレジスタ。この例にはコマンドの成功を検証するための読み出しがオプションで含まれています。
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Select the 1-Wire channel on a DS2482-800.
//
// Returns: TRUE if channel selected
// FALSE device not detected or failure to perform select
//
int DS2482_channel_select(int channel)
{
unsigned char ch, ch_read, check;
// Channel Select (Case A)
// S AD,0 [A] CHSL [A] CC [A] Sr AD,1 [A] [RR] A\ P
// [] indicates from slave
// CC channel value
// RR channel read back
I2C_start();
I2C_write(I2C_address | I2C_WRITE, EXPECT_ACK);
I2C_write(CMD_CHSL, EXPECT_ACK);
switch (channel)
{
default: case 0: ch = 0xF0; ch_read = 0xB8; break;
case 1: ch = 0xE1; ch_read = 0xB1; break;
case 2: ch = 0xD2; ch_read = 0xAA; break;
case 3: ch = 0xC3; ch_read = 0xA3; break;
case 4: ch = 0xB4; ch_read = 0x9C; break;
case 5: ch = 0xA5; ch_read = 0x95; break;
case 6: ch = 0x96; ch_read = 0x8E; break;
case 7: ch = 0x87; ch_read = 0x87; break;
};
I2C_write(ch, EXPECT_ACK);
I2C_rep_start();
I2C_write(I2C_address | I2C_READ, EXPECT_ACK);
check = I2C_read(NACK);
I2C_stop();
// check for failure due to incorrect read back of channel
return (check == ch_read);
}
例4. DS2482-800チャネルセレクト
DS2482の1-Wireオペレーション
OWReset
1-Wire Resetコマンド(B4h)は、1-Wireネットワークにて1-Wireリセットを、1-Wireデバイスプレゼンスパルスのサンプルを生成します。このサンプルのステータスはステータスレジスタ内のPresence-Pulse Detect (PPD)およびShort Detected (SD)フィールドで、レポートされます。図6は1-Wire ResetコマンドのI2C通信を示します。例5はCのプレゼンスパルスのためにチェックされた送信コマンドとステータスレジスタを示します。

図6. 1-Wireリセット。1-Wire通信を開始または終了します。1-Wire Idle (1WB = 0)、1-Wireコマンドが終了するまでビジーポーリング、その後に結果を読み出します。
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Reset all of the devices on the 1-Wire Net and return the result.
//
// Returns: TRUE(1): presence pulse(s) detected, device(s) reset
// FALSE(0): no presence pulses detected
//
int OWReset(void)
{
unsigned char status;
int poll_count = 0;
// 1-Wire reset (Case B)
// S AD,0 [A] 1WRS [A] Sr AD,1 [A] [Status] A [Status] A\ P
// \--------/
// Repeat until 1WB bit has changed to 0
// [] indicates from slave
I2C_start();
I2C_write(I2C_address | I2C_WRITE, EXPECT_ACK);
I2C_write(CMD_1WRS, EXPECT_ACK);
I2C_rep_start();
I2C_write(I2C_address | I2C_READ, EXPECT_ACK);
// loop checking 1WB bit for completion of 1-Wire operation
// abort if poll limit reached
status = I2C_read(ACK);
do
{
status = I2C_read(status & STATUS_1WB);
}
while ((status & STATUS_1WB) && (poll_count++ < POLL_LIMIT));
I2C_stop();
// check for failure due to poll limit reached
if (poll_count >= POLL_LIMIT)
{
// handle error
// ...
DS2482_reset();
return FALSE;
}
// check for short condition
if (status & STATUS_SD)
short_detected = TRUE;
else
short_detected = FALSE;
// check for presence detect
if (status & STATUS_PPD)
return TRUE;
else
return FALSE;
}
例5. OWResetコード
OWWriteBit/OWReadBit
1-Wireビットコマンド(0x87)はシングル1-Wireビットタイムスロットを生成します。図7は1-WireシングルビットコマンドケースのI2C通信コードを示します。図8はVが送信ビットであるビット割り当てバイトです。例6はOWWriteBit、OWReadBit、およびOWTouchBitコードを示します。

図7. 1-Wire Single Bit。1-Wireライン上でシングルタイムスロットを生成します。1WBが1から0に変わると、Statusレジスタは1-Wireシングルビットコマンドの有効結果を保持します。

図8. 1-Wireシングルデータバイト
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Send 1 bit of communication to the 1-Wire Net.
// The parameter 'sendbit' least significant bit is used.
//
// 'sendbit' - 1 bit to send (least significant byte)
//
void OWWriteBit(unsigned char sendbit)
{
OWTouchBit(sendbit);
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Reads 1 bit of communication from the 1-Wire Net and returns the
// result
//
// Returns: 1 bit read from 1-Wire Net
//
unsigned char OWReadBit(void)
{
return OWTouchBit(0x01);
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Send 1 bit of communication to the 1-Wire Net and return the
// result 1 bit read from the 1-Wire Net. The parameter 'sendbit'
// least significant bit is used and the least significant bit
// of the result is the return bit.
//
// 'sendbit' - the least significant bit is the bit to send
//
// Returns: 0: 0 bit read from sendbit
// 1: 1 bit read from sendbit
//
unsigned char OWTouchBit(unsigned char sendbit)
{
unsigned char status;
int poll_count = 0;
// 1-Wire bit (Case B)
// S AD,0 [A] 1WSB [A] BB [A] Sr AD,1 [A] [Status] A [Status] A\ P
// \--------/
// Repeat until 1WB bit has changed to 0
// [] indicates from slave
// BB indicates byte containing bit value in msbit
I2C_start();
I2C_write(I2C_address | I2C_WRITE, EXPECT_ACK);
I2C_write(CMD_1WSB, EXPECT_ACK);
I2C_write(sendbit ? 0x80 : 0x00, EXPECT_ACK);
I2C_rep_start();
I2C_write(I2C_address | I2C_READ, EXPECT_ACK);
// loop checking 1WB bit for completion of 1-Wire operation
// abort if poll limit reached
status = I2C_read(ACK);
do
{
status = I2C_read(status & STATUS_1WB);
}
while ((status & STATUS_1WB) && (poll_count++ < POLL_LIMIT));
I2C_stop();
// check for failure due to poll limit reached
if (poll_count >= POLL_LIMIT)
{
// handle error
// ...
DS2482_reset();
return 0;
}
// return bit state
if (status & STATUS_SBR)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
例6. 1-Wireシングルビットコード
OWWriteByte
1-Wire書き込みバイトコマンド(A5h)は1-Wireバスにシングルデータバイトを書き込みます。1-WireアクティビティはDS2482がこのコマンドを処理できる前に終了している必要があります。図9はI2C書き込み1-Wireバイトシーケンスを示します。コード例7は、このオペレーションから戻る前に1-Wireアクティビティが終了していることをチェックします。

図9. 1-Wire Write Byte。コマンドコードを1-Wireラインに送ります。1WBが1から0に変わると、1-Wire Write Byteコマンドが終了します。
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Send 8 bits of communication to the 1-Wire Net and verify that the
// 8 bits read from the 1-Wire Net are the same (write operation).
// The parameter 'sendbyte' least significant 8 bits are used.
//
// 'sendbyte' - 8 bits to send (least significant byte)
//
// Returns: TRUE: bytes written and echo was the same
// FALSE: echo was not the same
//
void OWWriteByte(unsigned char sendbyte)
{
unsigned char status;
int poll_count = 0;
// 1-Wire Write Byte (Case B)
// S AD,0 [A] 1WWB [A] DD [A] Sr AD,1 [A] [Status] A [Status] A\ P
// \--------/
// Repeat until 1WB bit has changed to 0
// [] indicates from slave
// DD data to write
I2C_start();
I2C_write(I2C_address | I2C_WRITE, EXPECT_ACK);
I2C_write(CMD_1WWB, EXPECT_ACK);
I2C_write(sendbyte, EXPECT_ACK);
I2C_rep_start();
I2C_write(I2C_address | I2C_READ, EXPECT_ACK);
// loop checking 1WB bit for completion of 1-Wire operation
// abort if poll limit reached
status = I2C_read(ACK);
do
{
status = I2C_read(status & STATUS_1WB);
}
while ((status & STATUS_1WB) && (poll_count++ < POLL_LIMIT));
I2C_stop();
// check for failure due to poll limit reached
if (poll_count >= POLL_LIMIT)
{
// handle error
// ...
DS2482_reset();
}
}
例7. OWWriteByteコード
OWReadByte
1-Wire読み込みバイトコマンド(96h)は1-Wireネットワークからシングルバイトを読み込みます。1-WireアクティビティはDS2482がこのコマンドを処理する前に終了している必要があります。図10はI2Cシーケンスを示します。1-Wire Read Byte Commandのコードは、コード例8にあります。1-Wireアクティビティは、終了し結果が返されたことを検証するために、読み込みバイトコマンドを発行した後にチェックされます。

図10. 1-Wire Read Byte。1-Wireネットワークからバイトを読み込みます。1WBビットが1から0に変わるまでStatusレジスタをポーリングします。その後、読み込みポインタをRead Dataレジスタ(コードE1h)に設定し、デバイスに再度アクセスして1-Wireネットワークから取得したデータバイトを読み出します。
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Send 8 bits of read communication to the 1-Wire Net and return the
// result 8 bits read from the 1-Wire Net.
//
// Returns: 8 bits read from 1-Wire Net
//
unsigned char OWReadByte(void)
{
unsigned char data, status;
int poll_count = 0;
// 1-Wire Read Bytes (Case C)
// S AD,0 [A] 1WRB [A] Sr AD,1 [A] [Status] A [Status] A // \--------/
// Repeat until 1WB bit has changed to 0
// Sr AD,0 [A] SRP [A] E1 [A] Sr AD,1 [A] DD A\ P
//
// [] indicates from slave
// DD data read
I2C_start();
I2C_write(I2C_address | I2C_WRITE, EXPECT_ACK);
I2C_write(CMD_1WRB, EXPECT_ACK);
I2C_rep_start();
I2C_write(I2C_address | I2C_READ, EXPECT_ACK);
// loop checking 1WB bit for completion of 1-Wire operation
// abort if poll limit reached
status = I2C_read(ACK);
do
{
status = I2C_read(status & STATUS_1WB);
}
while ((status & STATUS_1WB) && (poll_count++ < POLL_LIMIT));
// check for failure due to poll limit reached
if (poll_count >= POLL_LIMIT)
{
// handle error
// ...
DS2482_reset();
return 0;
}
I2C_rep_start();
I2C_write(I2C_address | I2C_WRITE, EXPECT_ACK);
I2C_write(CMD_SRP, EXPECT_ACK);
I2C_write(0xE1, EXPECT_ACK);
I2C_rep_start();
I2C_write(I2C_address | I2C_READ, EXPECT_ACK);
data = I2C_read(NACK);
I2C_stop();
return data;
}
例8. OWReadByteコード
OWBlock
OWBlockオペレーションは1-Wireバイトオペレーショングループを実行します。これは1-Wireネットワーク上のデータブロックを転送する際に有用です。例9はOWBlockのコード例を示します。
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// The 'OWBlock' transfers a block of data to and from the
// 1-Wire Net. The result is returned in the same buffer.
//
// 'tran_buf' - pointer to a block of unsigned
// chars of length 'tran_len' that will be sent
// to the 1-Wire Net
// 'tran_len' - length in bytes to transfer
//
void OWBlock(unsigned char *tran_buf, int tran_len)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < tran_len; i++)
tran_buf[i] = OWTouchByte(tran_buf[i]);
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Send 8 bits of communication to the 1-Wire Net and return the
// result 8 bits read from the 1-Wire Net. The parameter 'sendbyte'
// least significant 8 bits are used and the least significant 8 bits
// of the result are the return byte.
//
// 'sendbyte' - 8 bits to send (least significant byte)
//
// Returns: 8 bits read from sendbyte
//
unsigned char OWTouchByte(unsigned char sendbyte)
{
if (sendbyte == 0xFF)
return OWReadByte();
else
{
OWWriteByte(sendbyte);
return sendbyte;
}
}
例9. OWBlockコード
OWSearch/1-Wire Tripletコマンド
1-Wire検索は1-Wireネットワーク上のデバイスの64ビットの固有の登録番号を見つけるために使用されます。固有の登録番号は、ROM (Read-Only Memory)にあるため、1-WireのデータシートではROM番号としてよく引用されます。検索は、検索コマンドの前の1-Wireリセットで開始します。全1-Wireデバイスが応答する検索コマンドはF0hです。検索コマンドの後、1-Wireマスタはバイナリ検索を行い1つのデバイスを見つけます。バイナリ検索は、最初にビットを読み込み、ビットの補数を読み込み、その後どのデバイスが検索にあるかを示すビットを書き込むことで、64ビットのそれぞれをみます。これらの3つのシングルビットシーケンスはTripletと呼ばれます。DS2482はこのTripletを実行することでより効率的に1-Wire検索を行うショートカットコマンドを備えています。
Tripletコマンド(78h)は3つのタイムスロット、2つの読み込みタイムスロット、1つの書き込みタイムスロットを1-Wireネットワーク上で生成します。Statusレジスタの方向バイト(DIR)は書き込みタイムスロット(図11)のタイプを決定します。例10では、1-Wire Tripletコマンドを使った1-Wire検索法一式を図示します。この例には、検索を設定し最初とその次のデバイスを見つける機能もあります。OWNextへの繰り返し呼び出しの前のOWFirst呼び出しは、1-Wireネットワーク上の全デバイスを見つけます。1-Wire検索アルゴリズムの説明については、アプリケーションノート187 「1-Wire検索アルゴリズム」をご参照ください。

図11. 1-Wire Triplet。1-Wireネットワーク上でSearch ROM機能を実行します。1-Wire機能の終了にはアイドル時間が必要です。その後、読み込みモードでデバイスにアクセスし1-Wire Tripletコマンドからの結果を入手してください。
// Search state
unsigned char ROM_NO[8];
int LastDiscrepancy;
int LastFamilyDiscrepancy;
int LastDeviceFlag;
unsigned char crc8;
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Find the 'first' devices on the 1-Wire network
// Return TRUE : device found, ROM number in ROM_NO buffer
// FALSE : no device present
//
int OWFirst()
{
// reset the search state
LastDiscrepancy = 0;
LastDeviceFlag = FALSE;
LastFamilyDiscrepancy = 0;
return OWSearch();
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Find the 'next' devices on the 1-Wire network
// Return TRUE : device found, ROM number in ROM_NO buffer
// FALSE : device not found, end of search
//
int OWNext()
{
// leave the search state alone
return OWSearch();
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// The 'OWSearch' function does a general search. This function
// continues from the previous search state. The search state
// can be reset by using the 'OWFirst' function.
// This function contains one parameter 'alarm_only'.
// When 'alarm_only' is TRUE (1) the find alarm command
// 0xEC is sent instead of the normal search command 0xF0.
// Using the find alarm command 0xEC will limit the search to only
// 1-Wire devices that are in an 'alarm' state.
//
// Returns: TRUE (1) : when a 1-Wire device was found and its
// Serial Number placed in the global ROM
// FALSE (0): when no new device was found. Either the
// last search was the last device or there
// are no devices on the 1-Wire Net.
//
int OWSearch()
{
int id_bit_number;
int last_zero, rom_byte_number, search_result;
int id_bit, cmp_id_bit;
unsigned char rom_byte_mask, search_direction, status;
// initialize for search
id_bit_number = 1;
last_zero = 0;
rom_byte_number = 0;
rom_byte_mask = 1;
search_result = FALSE;
crc8 = 0;
// if the last call was not the last one
if (!LastDeviceFlag)
{
// 1-Wire reset
if (!OWReset())
{
// reset the search
LastDiscrepancy = 0;
LastDeviceFlag = FALSE;
LastFamilyDiscrepancy = 0;
return FALSE;
}
// issue the search command
OWWriteByte(0xF0);
// loop to do the search
do
{
// if this discrepancy if before the Last Discrepancy
// on a previous next then pick the same as last time
if (id_bit_number < LastDiscrepancy)
{
if ((ROM_NO[rom_byte_number] & rom_byte_mask) > 0)
search_direction = 1;
else
search_direction = 0;
}
else
{
// if equal to last pick 1, if not then pick 0
if (id_bit_number == LastDiscrepancy)
search_direction = 1;
else
search_direction = 0;
}
// Perform a triple operation on the DS2482 which will perform
// 2 read bits and 1 write bit
status = DS2482_search_triplet(search_direction);
// check bit results in status byte
id_bit = ((status & STATUS_SBR) == STATUS_SBR);
cmp_id_bit = ((status & STATUS_TSB) == STATUS_TSB);
search_direction =
((status & STATUS_DIR) == STATUS_DIR) ? (byte)1 : (byte)0;
// check for no devices on 1-Wire
if ((id_bit) && (cmp_id_bit))
break;
else
{
if ((!id_bit) && (!cmp_id_bit) && (search_direction == 0))
{
last_zero = id_bit_number;
// check for Last discrepancy in family
if (last_zero < 9)
LastFamilyDiscrepancy = last_zero;
}
// set or clear the bit in the ROM byte rom_byte_number
// with mask rom_byte_mask
if (search_direction == 1)
ROM_NO[rom_byte_number] |= rom_byte_mask;
else
ROM_NO[rom_byte_number] &= (byte)~rom_byte_mask;
// increment the byte counter id_bit_number
// and shift the mask rom_byte_mask
id_bit_number++;
rom_byte_mask <<= 1;
// if the mask is 0 then go to new SerialNum byte rom_byte_number
// and reset mask
if (rom_byte_mask == 0)
{
calc_crc8(ROM_NO[rom_byte_number]); // accumulate the CRC
rom_byte_number++;
rom_byte_mask = 1;
}
}
}
while(rom_byte_number < 8); // loop until through all ROM bytes 0-7
// if the search was successful then
if (!((id_bit_number < 65) || (crc8 != 0)))
{
// search successful so set LastDiscrepancy,LastDeviceFlag
// search_result
LastDiscrepancy = last_zero;
// check for last device
if (LastDiscrepancy == 0)
LastDeviceFlag = TRUE;
search_result = TRUE;
}
}
// if no device found then reset counters so next
// 'search' will be like a first
if (!search_result || (ROM_NO[0] == 0))
{
LastDiscrepancy = 0;
LastDeviceFlag = FALSE;
LastFamilyDiscrepancy = 0;
search_result = FALSE;
}
return search_result;
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Use the DS2482 help command '1-Wire triplet' to perform one bit of a
//1-Wire search.
//This command does two read bits and one write bit. The write bit
// is either the default direction (all device have same bit) or in case of
// a discrepancy, the 'search_direction' parameter is used.
//
// Returns – The DS2482 status byte result from the triplet command
//
unsigned char DS2482_search_triplet(int search_direction)
{
unsigned char status;
int poll_count = 0;
// 1-Wire Triplet (Case B)
// S AD,0 [A] 1WT [A] SS [A] Sr AD,1 [A] [Status] A [Status] A\ P
// \--------/
// Repeat until 1WB bit has changed to 0
// [] indicates from slave
// SS indicates byte containing search direction bit value in msbit
I2C_start();
I2C_write(I2C_address | I2C_WRITE, EXPECT_ACK);
I2C_write(CMD_1WT, EXPECT_ACK);
I2C_write(search_direction ? 0x80 : 0x00, EXPECT_ACK);
I2C_rep_start();
I2C_write(I2C_address | I2C_READ, EXPECT_ACK);
// loop checking 1WB bit for completion of 1-Wire operation
// abort if poll limit reached
status = I2C_read(ACK);
do
{
status = I2C_read(status & STATUS_1WB);
}
while ((status & STATUS_1WB) && (poll_count++ < POLL_LIMIT));
I2C_stop();
// check for failure due to poll limit reached
if (poll_count >= POLL_LIMIT)
{
// handle error
// ...
DS2482_reset();
return 0;
}
// return status byte
return status;
}
例10. OWSearchコード
拡張1-Wireオペレーション
OWSpeed
例11に、DS2482を使って1-Wireネットワークの速度を変える方法を示します。全1-Wireデバイスは標準通信速度をデフォルト値とします。デバイスの中にはその後、デバイスOverdrive-Match-ROMまたはOverdrive-Skip-ROMコマンドを使って、オーバドライブ速度に移るべきか決定できるものもあります。デバイスが一度オーバドライブ速度になると、全1-Wire通信はオーバドライブで進むことができます。標準速度1-Wireリセットによってデバイスを標準速度に戻します。
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Set the 1-Wire Net communication speed.
//
// 'new_speed' - new speed defined as
// MODE_STANDARD 0x00
// MODE_OVERDRIVE 0x01
//
// Returns: current 1-Wire Net speed
//
int OWSpeed(int new_speed)
{
// set the speed
if (new_speed == MODE_OVERDRIVE)
c1WS = CONFIG_1WS;
else
c1WS = FALSE;
// write the new config
DS2482_write_config(c1WS | cSPU | cPPM | cAPU);
return new_speed;
}
例11. OWSpeedコード
OWLevel
例12は、DS2482を使って1-Wireネットワークのレベルを変える方法を示しています。DS2482は1-Wire通信ビットまたはバイトの後のみストロングプルアップをイネーブルします。そのため、OWLevelコードは1-Wireネットワークを標準プルアップに戻すことができるのみです。ストロングプルアップをイネーブルするには、OWWriteBytePowerまたはOWReadBitPowerオペレーションを使ってください。
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Set the 1-Wire Net line level pullup to normal. The DS2482 only
// allows enabling strong pullup on a bit or byte event. Consequently this
// function only allows the MODE_STANDARD argument. To enable strong pullup
// use OWWriteBytePower or OWReadBitPower.
//
// 'new_level' - new level defined as
// MODE_STANDARD 0x00
//
// Returns: current 1-Wire Net level
//
int OWLevel(int new_level)
{
// function only will turn back to non-strong pullup
if (new_level != MODE_STANDARD)
return MODE_STRONG;
// clear the strong pullup bit in the global config state
cSPU = FALSE;
// write the new config
DS2482_write_config(c1WS | cSPU | cPPM | cAPU);
return MODE_STANDARD;
}
例12. OWLevelコード
OWReadBitPower
例13は、1-Wireビットを読み込み電力分配を実行するOWReadBitPowerに使用されるコードを示しています。ConfigurationレジスタのStrong Pullup (SPU)ビットがイネーブルされると、DS2482は次のビットまたはバイト通信の後にアクティブに1-Wireネットワークをハイにプルします。このオペレーションはビット読み込みが期待された応答をしていることを確認します。応答が正しくない場合は1-Wireレベルは標準プルアップ状態に戻されます。
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Send 1 bit of communication to the 1-Wire Net and verify that the
// response matches the 'applyPowerResponse' bit and apply power delivery
// to the 1-Wire net. Note that some implementations may apply the power
// first and then turn it off if the response is incorrect.
//
// 'applyPowerResponse' - 1 bit response to check, if correct then start
// power delivery
//
// Returns: TRUE: bit written and response correct, strong pullup now on
// FALSE: response incorrect
//
int OWReadBitPower(int applyPowerResponse)
{
unsigned char rdbit;
// set strong pullup enable
cSPU = CONFIG_SPU;
// write the new config
if (!DS2482_write_config(c1WS | cSPU | cPPM | cAPU))
return FALSE;
// perform read bit
rdbit = OWReadBit();
// check if response was correct, if not then turn off strong pullup
if (rdbit != applyPowerResponse)
{
OWLevel(MODE_STANDARD);
return FALSE;
}
return TRUE;
}
例13. OWReadBitPowerコード
OWWriteBytePower
例14は、1-Wireバイトを書き込みストロングプルアップ電力分配を実行するOWWriteBytePowerに使われるコードを示しています。設定レジスタ内のStrong Pullup (SPU)ビットがイネーブルされると、DS2482は次のビットまたはバイト通信の後、アクティブに1-Wireネットワークをハイにプルします。その後、OWLevel機能が呼び出され1-Wireネットワークを標準プルアップに戻すことができます。
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Send 8 bits of communication to the 1-Wire Net and verify that the
// 8 bits read from the 1-Wire Net are the same (write operation).
// The parameter 'sendbyte' least significant 8 bits are used. After the
// 8 bits are sent change the level of the 1-Wire net.
//
// 'sendbyte' - 8 bits to send (least significant bit)
//
// Returns: TRUE: bytes written and echo was the same, strong pullup now on
// FALSE: echo was not the same
//
int OWWriteBytePower(int sendbyte)
{
// set strong pullup enable
cSPU = CONFIG_SPU;
// write the new config
if (!DS2482_write_config(c1WS | cSPU | cPPM | cAPU))
return FALSE;
// perform write byte
OWWriteByte(sendbyte);
return TRUE;
}
例14. OWWriteBytePowerコード
結論
DS2482は、I2Cバスを1-Wireネットワークにうまくブリッジします。このアプリケーションノートでは、I2C 1-WireラインドライバDS2482ファミリを使用した1-Wireアプリケーションインタフェースのソリューションの全てについて説明しました。このインタフェースによって、1つのデバイスが全1-Wireデバイスと通信可能です。サンプルコードはI2C通信ポートを備えるあらゆるホストシステムで容易に実行されます。C言語実行の一式もダウンロード可能です。このコードのテストプラットフォームはCMAXQUSBの評価キットでした。
改訂履歴
11/2005 Version 1.0-最初のリリース
9/2008 Version 2.0-より低レベルのI2C通信コールを使用するためサンプルコードを変更。それに伴い文章を改訂。