Selecting an ADC driver to achieve optimized signal chain performance
Selecting an ADC driver to achieve optimized signal chain performance
Jul 13 2015
The figure shows a high-precision, low-noise, 18-bit data-acquisition signal chain that features ±0.8-LSB integral nonlinearity (INL), ±0.5-LSB differential nonlinearity (DNL), and 99-dB signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). The AD7960 18-bit, 5-MSPS PulSAR differential ADC uses a capacitive digital-to-analog converter (CAPDAC) to provide unprecedented noise and linearity without latency or pipeline delay. It provides the wide bandwidth, high accuracy (100 dB DR), and fast sampling (200 ns) required for multiplexed applications, while significantly reducing power dissipation and cost in multichannel applications.

Precision, fast-settling signal chain using
AD7960, ADA4899, AD8031, and ADR4550
ADC Driver
The acquisition time of the ADC determines the settling time requirements for the ADC driver. The table shows some specifications that must be considered when selecting an ADC driver. As always, the signal chain performance should be verified on the bench to ensure that the desired performance is achievable.AD7960 ADC Driver Selection Benchmark
| ADC Driver Specifications | General Formula | Minimum Requirements |
| Bandwidth (f-3db_amp) |
 |
40MHz |
| Slew Rate |  |
100 V/µs |
| Settling Time | From data sheet |
100 ns |
| SNR |
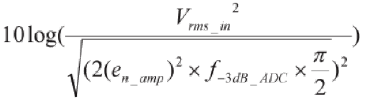 |
105.5 dB |
The op amp data sheet usually specifies the settling time as the combined time for linear settling and slewing; the formulas given are first-order approximations assuming 50% for linear settling and 50% for slewing (multiplexed application) using a 5-V single-ended input.
The ADA4899-1 rail-to-rail amplifier features 600-MHz bandwidth, –117-dBc distortion @ 1 MHz, and 1-nV/√Hz noise. It settles to 0.1% within 50 ns when configured as a unity-gain buffer driving the inputs of the AD7960 with a 5-V differential signal.
About the Authors
Maithil Pachchigar is a systems application engineer in the Industrial and Multimarkets Business Unit at Analog Devices, Inc., in Wilmington, MA. Since joining ADI in 2010, he has been focused on the precision signal chain...