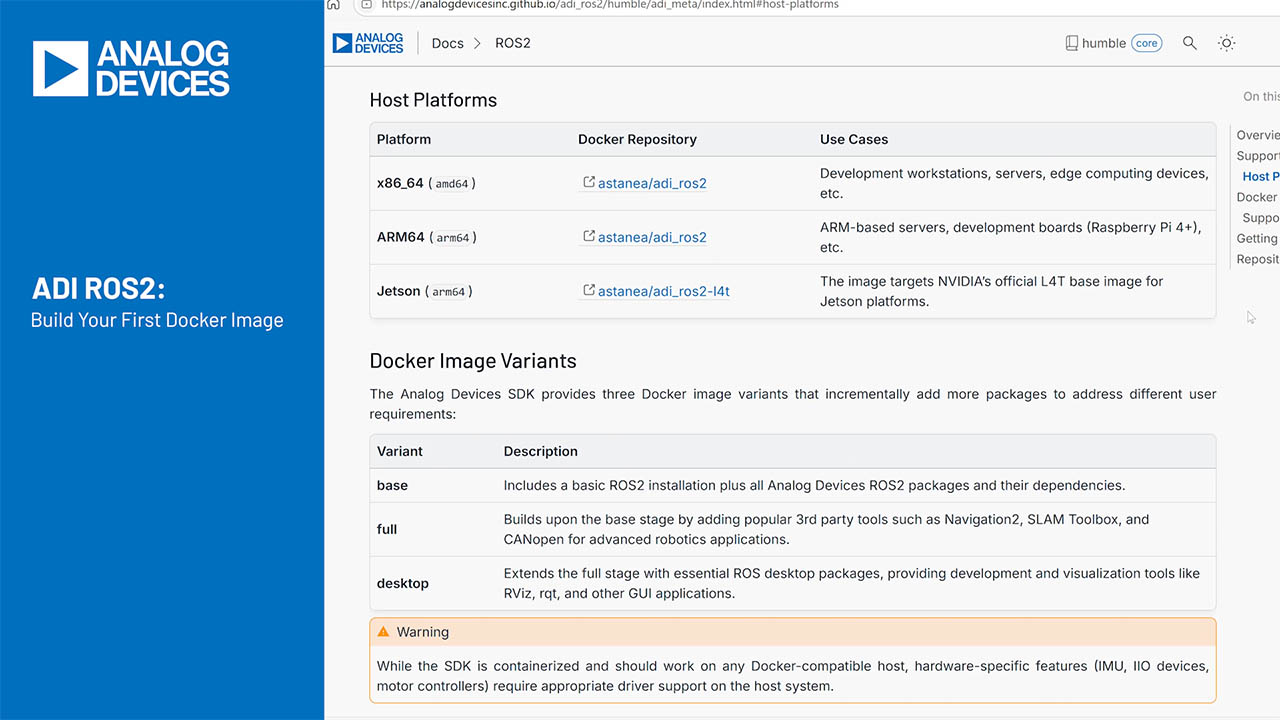
Abstract
A 1-Wire bus provides both communication and power between a host and slave devices on a single line. Some
Introduction
The 1-Wire bus is a simple signaling scheme that performs half-duplex bidirectional communications between a master controller and one or more slaves, all sharing a common data line. Both power delivery and data communication take place over this single line. Most 1-Wire devices use very little power, on the order of tens of microamps, to operate and communicate. Some 1-Wire devices, however, need more power during specific operations, such as an EEPROM write or a device-specific calculation or measurement. During these periods of increased power demand, it is important that the voltage on the 1-Wire bus does not fall below the device's minimum operating pullup voltage (VPUP). For most parasitic-powered 1-Wire devices, the minimum operating voltage (VPUP) is 2.8V.
1-Wire Devices that Need Extra Power
| Part | EEPROM | SHA-1 | Temperature | ADC |
| DS18B20 |  |
 |
||
| DS1920 |  |
 |
||
| DS1961S |  |
 |
||
| DS1971 |  |
|||
| DS1972 |  |
|||
| DS1973 |  |
|||
| DS1977 |  |
|||
| DS2431 |  |
|||
| DS2432 |  |
 |
||
| DS2450 |  |
|||
| DS28E01-100 |  |
 |
||
| DS28E04-100 |  |
|||
| DS28EA00 |  |
 |
||
| DS28EC20 |  |
How to Identify Extra Power Requirements in the EC Table
Any additional power requirements for a device are listed in the data sheet's electrical characteristics (EC) table under a variety of terms (Table 2). The pullup resistor's specification (RPUP) in the EC table is for 1-Wire communication only and does not include additional power requirements for the special operations.
| Parameter Description | Symbol | 1-Wire Device |
| Programming Current | IPROG | DS1961S, DS1972, DS2431, DS28E01, DS28E04, DS28E00 |
| Programming Current | ILPROG | DS1973, DS1977, DS2432 |
| Programming Current | IP | DS1971 (DS2430A) |
| SHA Computation Current | ILCSHA | DS1961S, DS28E01 |
| Active Current | IDD, IDQA | DS1920, DS18B20, DS18B20-PAR |
| Conversion Current | ICONV | DS28EA00 |
| Operating Current | ICC | DS2450 |

Figure 1. Example of the EC table for the DS28EA00.
Available Power
For a given VPUP and RPUP, the voltage difference between VPUP and the 1-Wire device's VPUPmin determines the current available for special functions. The available current can be calculated as
VPUP = 5V
RPUP = 2kΩ
VPUPmin = 2.8V, resulting in IAVAIL = 1.1mA
So for this example, there are 1.1mA available before the 1-Wire voltage drops below the minimum VPUP. If the available current is not sufficient for the application, then a lower pullup resistor or a low-impedance bypass to the pullup resistor will be necessary.
Finding the Right Pullup (RPUP)
The available current can be calculated by dividing the potential voltage drop from nominal VPUP to the minimum VPUP by the pullup resistor (RPUP). Figure 2 graphs this calculation based on a VPUP of 5V with a device that has a minimum VPUP of 2.8V. A pullup resistor of 2.2kΩ or less supports at least 1mA at 5V pullup voltage.

Figure 2. Available current for VPUP = 5V.
Similarly, Figure 3 shows the available current based on a VPUP of 3.3V. With only 0.5V as the permissible voltage drop on the pullup resistor, very little current is available. Other means of providing the extra current are probably required (see Low-Impedance Bypass section below).

Figure 3. Available current for VPUP = 3.3V.
Advanced Considerations
Choosing a very-low pullup resistor value delivers the desired power to run the special function. However, this configuration raises the voltage representing logic 0 on the 1-Wire bus. If VOL levels do not meet the minimum-voltage input low (VIL) specified for the 1-Wire slave or the 1-Wire master, then reliable communication will not be possible. The most common VOL specification for 1-Wire devices is 0.4V at 4mA, maximum. This value is equivalent to an impedance of 100Ω, maximum, when the 1-Wire device is responding with a logic 0. VIL varies from 0.3V to 0.8V, depending on the 1-Wire device. With multiple
(Note: Instead of starting the equation with 100Ω, one could write VOL/4mA.)
Therefore, assuming a VIL maximum of 0.4V, the results are
For a VPUP = 5V: 1150Ω
For VPUP = 3.3V: 725Ω
Assuming a VIL maximum of 0.3V, the results are
For a VPUP = 5V: 1567Ω
For VPUP = 3.3V: 1000Ω
The tolerances for the pullup resistor and the power supply must also be considered when selecting the proper pullup. These tolerances are not correlated, i.e., they can add up to either (positive, negative) side or cancel each other. Always check the worst combinations: voltage at upper limit with resistor at lower limit (i.e., highest VOL), and voltage lower limit with resistor at upper limit (i.e., lowest available extra current).
Low-Impedance Bypass
If meeting the VOL and VIL requirements requires a pullup resistor that cannot deliver the necessary current, then the extra current must be supplied by other means. There are two ways to do this:
- Implement a discrete low impedance bypass (also called a strong pullup) that is engaged only during high current demand.
- Utilize a 1-Wire interface device that incorporates a strong pullup.
Examples of a 1-Wire master with a discrete strong pullup can be found in application note 4206, "Choosing the Right 1-Wire® Master for Embedded Applications," or application note 244, "Advanced 1-Wire Network Driver." Figure 4 shows a strong pullup controlled with an extra IO pin.

Figure 4. Bidirectional port pin with optional circuit for strong pullup (dashed lines).
There are three 1-Wire interface chips that incorporate a strong pullup feature (Table 3). The DS2482-100 also has an external control signal that can be used to drive an additional discrete, extra-strong pullup.
| Device | Interface | Features |
| DS2480B | Serial | Strong pullup, active pullup |
| DS2482-100 | I²C | Single 1-Wire channel with built in strong pullup, optional active pullup, control signal for extra-strong pullup |
| DS2482-800 | I²C | Eight 1-Wire channels with built in strong pullup, optional active pullup |
Conclusion
For extended features like temperature conversion, EEPROM, or a SHA-1 engine to operate properly in 1-Wire devices, those devices must be provided with sufficient current from the 1-Wire master without allowing the 1-Wire to drop below the minimum-voltage pullup (VPUP). The 1-Wire pullup resistor (RPUP) must, therefore, be sized to provide this current in accordance with application demands. If application requirements do not permit a pullup resistor of the correct size, then the current can be supplied with a discrete strong pullup circuit or a 1-Wire interface chip such as the DS2480B or DS2482.
Related to this Article
Products
1Kb Protected 1-Wire EEPROM with SHA-1 Engine
iButton 1Kb EEPROM with SHA-1 Engine
1024-Bit 1-Wire EEPROM
1-Wire Quad A/D Converter
Econo 1-Wire Digital Thermometer
1-Wire Digital Thermometer with Sequence Detect and PIO
1-Wire Parasite-Power Digital Thermometer
1-Wire Parasite-Power Digital Thermometer
Parasite-Power Digital Thermometer
1-Wire Ambient Temperature Sensor
1-Wire Parasite-Power, Ambient Temperature Sensor
Programmable Resolution 1-Wire Digital Thermometer
Temperature iButton
1-Wire EEPROM
iButton 32KB EEPROM
20Kb 1-Wire EEPROM
1Kb Protected 1-Wire EEPROM with SHA-1 Engine
4096-Bit Addressable 1-Wire EEPROM with PIO
iButton 256-Bit EEPROM
iButton 4Kb EEPROM
iButton 1024-Bit EEPROM