Abstract
The DS2780 allows the user to customize the stand-alone battery fuel gauge to the exact requirements of the application and the cell being used. The parameters required are typically known in units such as mA, V, mAhrs, and mΩ. The DS2780 requires that the parameters are stored in units such as uV, uVhrs and mhos. This application note describes the calculations involved in converting the typical units into units that are stored in the device.
Introduction
The DS2780 standalone battery fuel gauge is simple to use and very accurate, assuming the correct parameters for the application have been stored in this device. It is very important that the correct data be stored so that the fuel gauge is optimized. The DS2780K provides an easy way to program the DS2780. The user can input characterization data of the cell and other application data in units such as mA, V, mAhrs, and mΩ, as shown in Figure 1. The DS2780K then converts that data into the correct format that actually gets stored to the device, as shown in Figure 2. Application note 3463, "Getting Started with the DS2780" describes how to select all of the parameters that are stored in the DS2780. The following text describes the calculations involved in storing the parameters to the device.
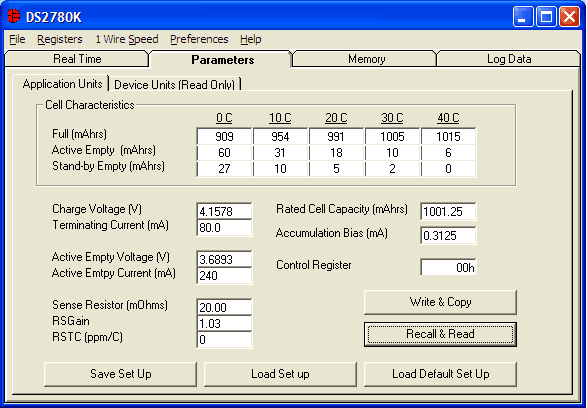
Figure 1. Application units sub-tab of parameters tab.

Figure 2. Device units sub-tab of parameters tab.
Calculations
Figure 1 shows the parameters that are needed by the DS2780 to operate accurately as a fuel gauge. When the Write & Copy button is clicked, the DS2780K software converts the parameters into the format that is actually stored in the device, as shown in Figure 2. Those values are then written and copied into the EEPROM Addresses 60h-7Ah.
The following sections show the calculations that are required to convert the application parameters into the actual values that are stored in the device at each address. The units used in the calculations are displayed such that AccBias_µV indicates the Accumulation Bias Register is displayed in terms of µV, and AccBias_mA indicates the same value in terms of mA. The value to be programmed to each EEPROM address is shown as a hexadecimal value in the form ValueStored (EEPROM ADDRESS); each shown is a single byte. Example data in the following calculations come from the values in Figure 1 that are plugged into the equations, which supply the values in Figure 2.
Control Register (Address 60h)
The Control Register is stored in Address 60h and the bits are formatted as described in the DS2780 data sheet. No calculations are required.
Accumulation Bias Register (Address 61h)
The Accumulation Bias Register is used to estimate battery currents that do not flow through the sense resistor, or battery self-discharge. This is a signed register with an LSB value of 1.5625µV/RSNS. It is stored in Address 61h, and has a range of -200.000µV to 198.4375µV. Assuming the Sense Resistor has a value of 20mΩ, the range is -10mA to 9.921875mA in 78.125µA steps.

Aging Capacity Register (Address 62h-63)
The Aging Capacity Register stores the rated capacity used in estimating the decrease in battery capacity during normal use. It is an unsigned register with an LSB value of 6.25µVhr/RSNS. It is stored in Addresses 62h and 63h, and has a range of 0µVhrs to 409.59375mVhrs. Assuming the Sense Resistor has a value of 20mΩ, the range is 0mAhrs to 20479.68755mAhrs in 0.3125mAhrs steps.

Charge Voltage Register (Address 64h)
The Charge Voltage Register stores the charge voltage threshold used to detect a fully charged state. This is an unsigned register with an LSB value of 19.52mV. It is stored in Address 64h, and has a range of 0 to 4.9776V.

Minimum Charge Current Register (Address 65h)
The Minimum Charge Current Register stores the charge current threshold that detects a fully charged state. This is an unsigned register with an LSB value of 50µV. It is stored in Address 65h, and has a range of 0 to 12.75mV. Assuming the Sense Resistor has a value of 20mΩ, the range is 0mA to 637.5mA in 2.5mA steps.

Active Empty Voltage Register (Address 66h)
The Active Empty Voltage Register stores the voltage threshold used to detect the Active Empty point. This is an unsigned register with an LSB value of 19.52mV. It is stored in Address 66h, and has a range of 0 to 4.9776V.

Active Empty Current Register (Address 67h)
The Active Empty Current Register stores the discharge current threshold that detects the Active Empty point. This is an unsigned register with an LSB value of 200µV. It is stored in Address 67h, and has a range of 0 to 51.2mV. Assuming the Sense Resistor has a value of 20mΩ, the range is 0mA to 2560mA in 10mA steps.

Active Empty 40 Register (Address 68h)
The Active Empty 40 Register stores the Active Empty point value for +40°C (as shown in Figure 11 of the DS2780 data sheet). This is an unsigned register with an LSB value of parts per million of the Full point at +40°C. It is stored in Address 68h, and has a range of 0 to 24.9% of the Full point for +40°C.
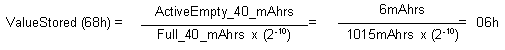
Sense Resistor Prime Register (Address 69h)
The Sense Resistor Prime (RSNSP) Register stores the value of the Sense Resistor that computes the absolute capacity results. This is an unsigned register with an LSB value of 1mhos. It is stored in Address 69h, and has a range of 1mhos to 255mhos, which is 1Ω to 3.922mΩ.

Full 40 Register (Address 6Ah-6Bh)
The Full 40 Register stores the Full point value for +40°C (Figure 11 of the DS2780 data sheet). This is an unsigned register with an LSB value of 6.25µVhr/RSNS. It is stored in Addresses 6Ah and 6Bh, and has a range of 0µVhrs to 409.59375mVhrs/RSNS. Assuming the Sense Resistor has a value of 20mΩ, the range is 0mAhrs to 20479.6785mAhrs in 0.3125mAhr steps.

Full Slopes (Address 6Ch-6Fh)
The Full point at +40°C is a stored value (Full 40), and the Full points at the other temperatures are calculated using the slope of the Full line (Figure 11 of the DS2780 data sheet). The slope for each 10-degree segment of the Full line is stored as an unsigned byte in terms of parts per million per °C (ppm/°C). It is assumed that the Full point at +40°C is the highest point on the Full line. The Full line is reconstructed in one-degree increments so that the Full point at any temperature is always less than or equal to the Full point at the next higher temperature. The slope can range from 0 to 15564ppm/°C.

Active Empty Slopes (Address 70h-73h)
The Active Empty line is reconstructed in a similar fashion as the Full line. The Active Empty point at +40°C is a stored value (Active Empty 40), and the Active Empty points at other temperatures are calculated from the slope between each 10-degree step. The slopes between each of the Active Empty points are stored as an unsigned byte in ppm/°C. The Active Empty line is reconstructed in one-degree increments so that the Active Empty point at any temperature is always greater than or equal to the Active Empty point at the next higher temperature. The slope can range from 0 to 15564ppm/°C.

Standby Empty Slopes (Address 74h-77h)
The Standby Empty line is reconstructed similarly to the Full and Active Empty lines. The Standby Empty point at +40°C is fixed at 0mAhrs. The Standby Empty points at other temperatures are calculated from the slope between each 10-degree step. The slopes between each of the Standby Empty points are stored as an unsigned byte in ppm/°C. The Standby Empty line is reconstructed in one-degree increments so that the Standby Empty point at any temperature is always greater than or equal to the Standby Empty point at the next higher temperature. The slope can range from 0 to 15564ppm/°C.

Sense Resistor Gain Register (Address 78h-79h)
The Sense Resistor Gain (RSGAIN) Register stores the calibration factor that produces accurate readings in the Current Register when a reference voltage is forced across SNS and VSS. This is an 11-bit value with an LSB value of 1/1024. It is stored in Addresses 78h and 79h, and has a range of 0 to 1.999. The nominal value for this register is 1.000.

Sense Resistor Temperature Coefficient Register (Address 7Ah)
The Sense Resistor Temperature Coefficient (RSTCO) Register stores the temperature coefficient of the sense resistor. This is an 8-bit value with an LSB value of 30.5176ppm/°C. It is stored in Address 7Ah, and has a range of 0 to 7782ppm/°C. A value of 0 disables the temperature-compensation function.

Conclusion
The DS2780 allows the user to customize the fuel gauge to the exact parameters of the application. However, the units stored in the device are not units that are commonly used. By following the calculations outlined in this application note, the more recognizable units can be converted into the units required by the DS2780.