Triple Output LED Driver Delivers 3000:1 Dimming Ratio in Buck, Boost or Buck-Boost Mode
Triple Output LED Driver Delivers 3000:1 Dimming Ratio in Buck, Boost or Buck-Boost Mode
by
Bin Zhang
2007-06-01
Introduction
The LT3496 is a triple output DC/DC converter designed for high performance, True Color PWM™ dimming in multichannel LED lighting applications. By integrating three independent driver channels, the LT3496 provides a space-saving and cost-efficient solution to drive multiple LED strings. Figure 1 shows a 50W LT3496 3-channel LED driver that occupies 350mm2 and with a sub-1.5mm profile.
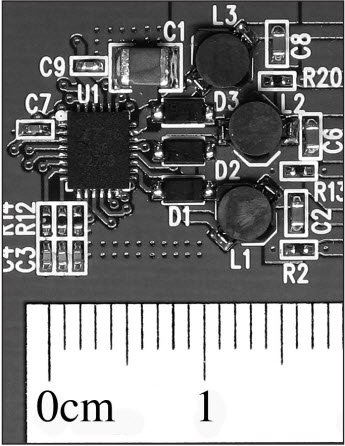
Figure 1. A complete LT3496 LED driver fits into 350mm2.
The LT3496 features high side current sensing and built-in gate drivers for PMOS high side LED disconnect (patent pending). These two features give the LT3496 its versatility, allowing it to drive LEDs to high PWM dimming ratio in buck, boost, or buck-boost configurations. The 45V capability of the internal power switch, 3V–40V input voltage range, and adjustable frequency result in reliable operation over a wide range of supply and output voltages. Applications for the LT3496 include RGB lighting, billboards and large displays, automotive and avionic lighting, and constant-current sources.
High Side LED Disconnect with High Side Current Sensing for System Versatility, Simplicity and Reliability
The LT3496’s high side LED disconnect and high side current sensing enable 3000:1 dimming control in buck, boost, or buck-boost configurations. No traditional LED driver can match the simplicity and high PWM dimming performance of LT3496, especially in buck-boost mode. Implementation of a high side disconnect switch with traditional LED drivers is possible, but uses many additional components, has slow response and burns extra power.
Because the LED disconnect and current sensing are on the high side of each LED string, the low sides of the LED strings can be tied together in boost or buck-boost mode to reduce the number of wires returning to the LED driver. In a boost configuration, each of the low side connections can be returned to ground anywhere, allowing a simple 1-wire LED connection for each LED string. Traditional LED drivers employ a low side LED disconnect approach, in which both the high side and the low side of each LED string must connect to the LED driver. Figure 2a shows simplified traditional boost LED drivers, where M1–M3 are LED-disconnect NMOS switches. Figure 2b shows a simplified LT3496 triple boost LED driver, where M1–M3 are LED-disconnect PMOS switches. The LT3496 solution removes three wires, increasing system simplicity and reliability. These advantages will become increasingly important as the channels are multiplied in high performance displays.
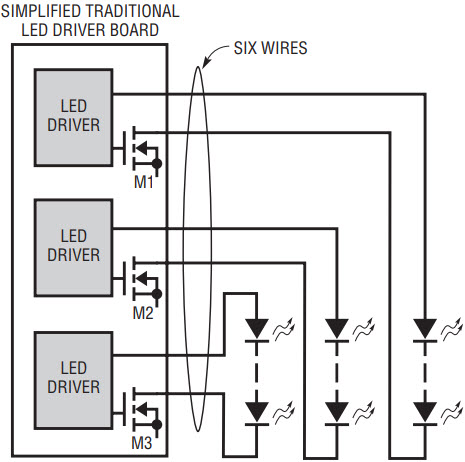
a. Traditional boost LED driver.
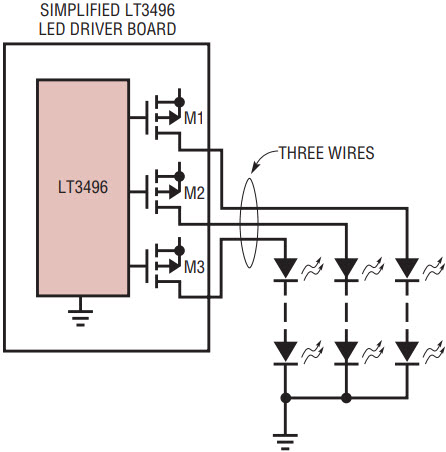
b. LT3496-based boost LED driver.
Figure 2. An LT3496-based boost LED driver requires half as many wires as a traditional boost LED driver.
Applications
Buck Mode LED Driver
The LT3496 can be configured as a buck mode LED driver for applications where the LED voltage is lower than the supply voltage. Figure 3 shows an LT3496 RGB driver for a large TFT LCD TV.
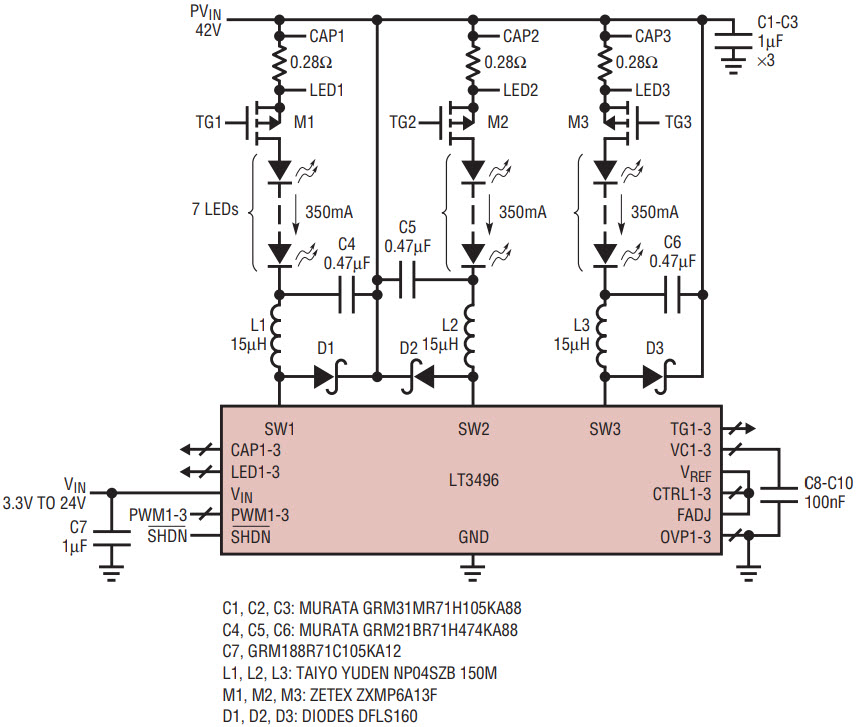
Figure 3. The LT3496 RGB driver for large TFT LCD TVs.
The three LT3496 channels operate independently, but function in the same way. For simplicity, the PWM operation of channel 1 is described here. If the PWM1 pin is pulled low, M1 is turned off, disconnecting the LED string of channel 1 and stopping the current draw from output capacitor C4. The VC1 pin is also disconnected from the compensation capacitor C8. C4 stores the state of the LED voltage and C8 stores the state of the LED current until PWM1 is pulled up again. This leads to a highly linear relationship between pulse width and output light, a large and accurate dimming range, and high efficiency. At 120Hz PWM frequency, the PWM control of the circuit allows 5000:1 dimming as shown in Figure 4. Figure 5 shows the efficiency as a function of the PWM duty cycle.
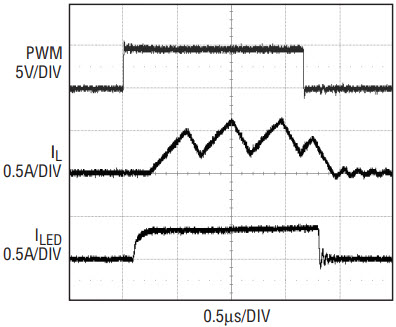
Figure 4. 5000:1 dimming waveforms for the application circuit of Figure 3.
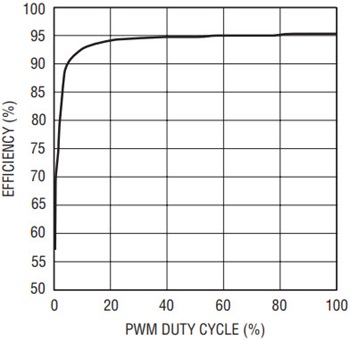
Figure 5. Efficiency of the application circuit of Figure 3.
Buck-Boost Mode LED Driver
In some LED applications, the desired supply voltage range and LED voltage range overlap, thus requiring buck-boost mode configuration. Figure 6 shows a LT3496 buck-boost mode LED driver for automotive lighting. The LED voltage is 9V–12V and the automobile battery voltage is 8V–30V. R1–R6 set the overvoltage protection voltage at 40V to guarantee the voltages of SW1–SW3, CAP1–CAP3, LED1–LED3, and TG1–TG3 pins are below the maximum rating voltage. R7–R8 set the switching frequency at 1.3MHz to limit the LT3496 power dissipation and ensure that a junction temperature of 125°C is not exceeded. Figure 7 shows the 3000:1 PWM dimming waveforms at 120Hz PWM frequency.
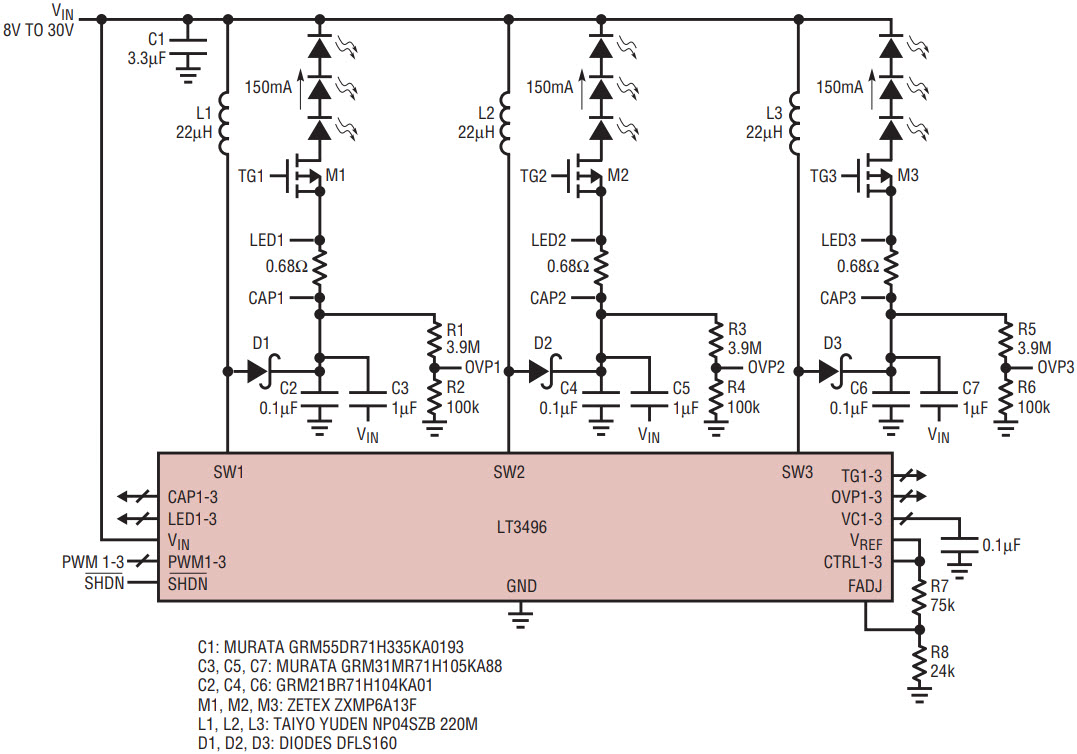
Figure 6. Buck-boost mode LED driver for automotive lighting.
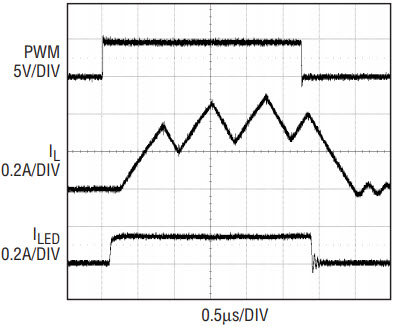
Figure 7. 3000:1 dimming waveforms for the application circuit of Figure 6.
Boost LED driver
The LT3496 can be configured as a boost LED driver for the applications where the LED voltage is higher than the supply voltage. Figure 8 shows a LT3496 boost LED driver for automotive lighting. D4, Q1–Q3, and R1–R4 create the battery surge voltage protection circuits to protect the LED string from being damaged by a battery surge voltage. The zener breakdown voltage of D4 is chosen to be lower than the LED voltage. When the VIN surge voltage increases to be close to the LED voltage, D4 breaks down and turns on Q1–Q3. Q1–Q3 pull PWM1–3 low and M1–M3 are turned off immediately to disconnect the LED strings from the LED driver.
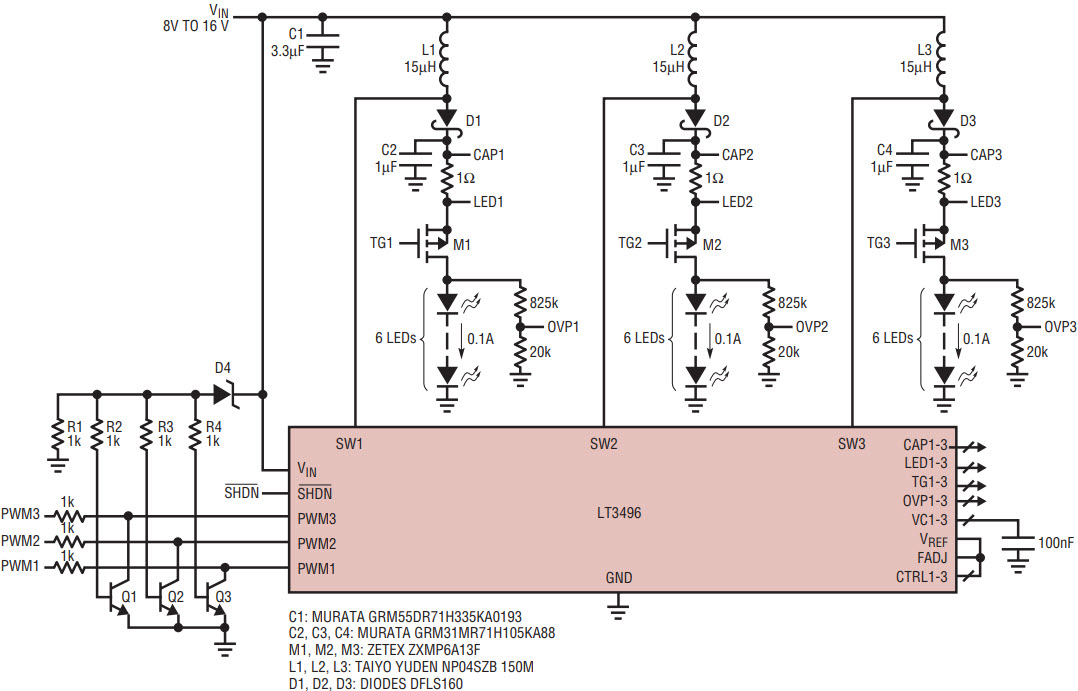
Figure 8. Boost mode LED driver with battery surge voltage protection for automotive lighting.
Figure 9 shows the 3000:1 PWM dimming waveforms at 120Hz PWM frequency.
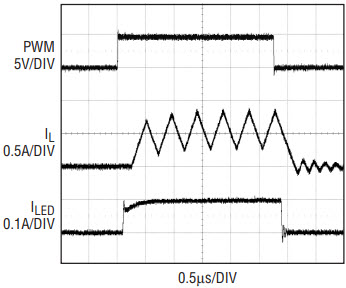
Figure 9. 3000:1 dimming waveforms for the application circuit of Figure 8.
Conclusion
The LT3496 provides a compact, low cost, high reliability, and high efficiency solution to multichannel LED lighting. With the capability of operating in buck, boost and buck-boost mode, the LT3496 LED driver delivers 3000:1 True Color PWM™ dimming ratio over a wide range of supply and output voltages.