Synchronous Buck Controller in 3mm × 3mm QFN Fits Automotive and Industrial Applications with 4V–38V Input Capability
Synchronous Buck Controller in 3mm × 3mm QFN Fits Automotive and Industrial Applications with 4V–38V Input Capability
by
Mark Mercer
2008-09-01
Introduction
The LTC3851 is a versatile synchronous step-down switching regulator controller that is available in a space saving 16-lead 3mm × 3mm QFN or convenient narrow SSOP packages. Its wide input range of 4V to 38V makes it well-suited for regulating power from a variety of sources, including automotive batteries, 24V industrial supplies and unregulated wall transformers. The strong onboard drivers allow the use of high power external MOSFETs to produce output currents up to 20A with output voltages ranging from 0.8V to 5.5V.
The constant frequency peak current mode control architecture provides excellent line and load regulation along with load current sharing capability and dependable cycle-by-cycle current limiting. OPTI-LOOP® compensation simplifies loop stability design and provides well-behaved regulation over a broad range of operating conditions. The LTC3851 has ±1% output voltage tolerance over temperature. The part’s low minimum on-time (90ns, typical) allows for low duty cycle operation even with switching frequencies as high as 750kHz.
Two Current Sensing Options
The LTC3851 features a high input impedance current sense comparator. This allows the use of the inductor’s DC resistance (DCR) as the current sense element in conjunction with an RC filter. DCR current sensing allows the designer to eliminate the need for a discrete sense resistor, thereby maximizing efficiency and lowering solution cost. Alternately, higher current sense accuracy may be achieved by connecting the SENSE+ and SENSE– pins to a precision sense resistor in series with the inductor. The LTC3851 offers the choice of three pin-selectable maximum current sense thresholds (30mV, 50mV and 75mV) to accommodate a wide range of DCR values and output current levels.
As with all constant frequency, peak current mode control switching regulators, the LTC3851 utilizes slope compensation to prevent sub-harmonic oscillations at high duty cycles. This is accomplished internally by adding a compensating ramp to the inductor current signal. Normally, this results in a >40% reduction of maximum inductor peak current at high duty cycles. However, the LTC3851 uses a novel scheme that allows the maximum peak inductor current to remain stable throughout all duty cycles.
Versatility
During heavy load operation, the LTC3851 operates in constant frequency, continuous conduction mode. At light loads, it can be configured to operate in high efficiency Burst Mode® operation, constant frequency pulse-skipping mode or forced continuous conduction mode. Burst Mode operation offers the highest efficiency because energy is transferred from the input to the output in pulse trains of one to several cycles. During the intervening period between pulse trains, the top and bottom MOSFETs are turned off and only the output capacitor provides current to the load. Forced continuous conduction mode results in the lowest output voltage ripple, but is the least efficient at light loads. Pulse-skipping mode offers a compromise—lower output ripple than Burst Mode operation and more efficiency than continuous conduction mode.
The switching frequency of the LTC3851 may be programmed from 250kHz to 750kHz by the resistor, RFREQ, connected to the FREQ/PLLFLTR pin. This provides the flexibility needed to optimize efficiency. Figure 1 shows a plot of the switching frequency vs RFREQ. Additionally, the switching frequency may be synchronized to an external clock. While doing so, the LTC3851 will operate in forced continuous conduction mode.
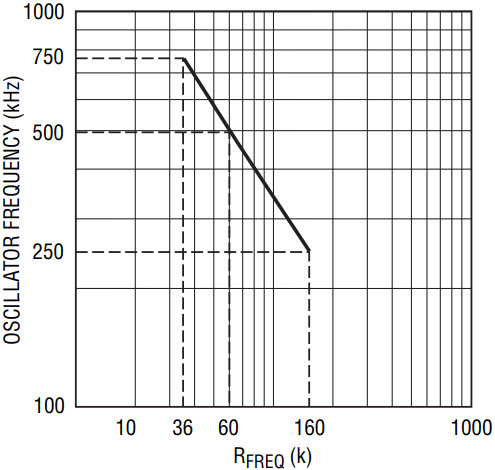
Figure 1. Relationship between oscillator frequency and resistor connected between FREQ/PLLFLTR and GND.
The output voltage can be ramped during start-up by means of an adjustable soft-start function, or it can track an external ramp signal. Track and soft-start control are combined in a single pin, TK/SS. Whenever TK/SS is less than 0.64V, the LTC3851 operates in pulse-skipping mode. This feature allows for starting up into a pre-biased load. When TK/SS is between 0.64V and 0.74V, the regulator operates in forced continuous mode to ensure a smooth transition from start-up to steady state. Once TK/SS exceeds 0.74V, the mode of operation is determined by the state of the MODE/PLLIN pin.
The RUN pin enables or disables the LTC3851. This pin has a precision 1.22V turn-on threshold which is useful for power supply sequencing. The turn-off threshold is 1.10V. There is an internal 2µA pull-up current source on the RUN pin.
The LTC3851’s fault protection features include foldback current limiting, output overvoltage detection and input undervoltage detection. If an overload event causes the output to fall to less than 40% of the target regulation value, then the LTC3851 folds back the maximum current sense threshold. This reduces the on-time in order to minimize power dissipation in the top MOSFET. If the output voltage is more than 10% above the target regulation value, the bottom MOSFET turns on until the output falls back into regulation. If the input voltage is allowed to fall low enough such than the output of the internal linear regulator falls below 3.2V, then switching operation is disabled. This feature protects against insufficient turn-on voltage for the top MOSFET.
3.3V/15A Regulator with DCR Sensing
Figure 2 shows a 400kHz, 3.3V output regulator using DCR current sensing. The DC resistance of the inductor is used as the current sense element, eliminating the need for a discrete sense resistor and thus maximizing efficiency. Figure 3 shows a plot of the efficiency vs load for all three modes of operation with an input voltage of 12V.
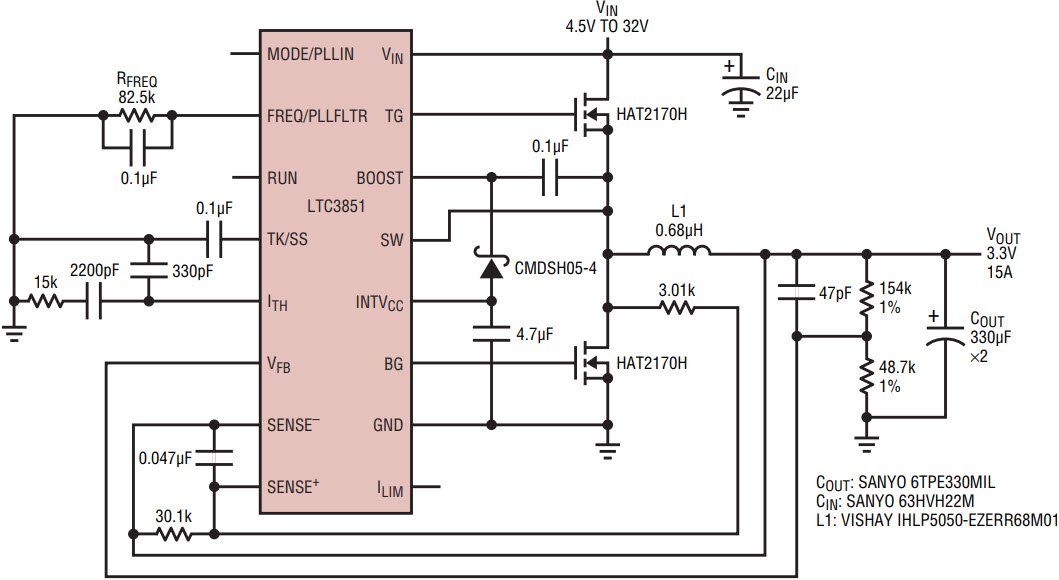
Figure 2. High efficiency 3.3V/15A power supply with DCR sensing.
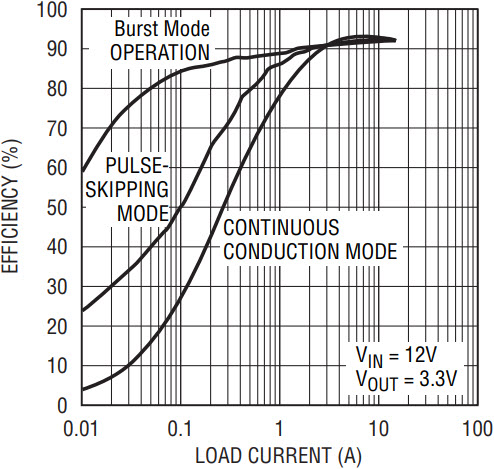
Figure 3. Efficiency vs load current with three modes of operation for the circuit of Figure 2.
1.5V/15A Regulator Synchronized at 350kHz
Figure 4 illustrates a 1.5V output regulator that is synchronized to an external clock. The loop filter components connected to the FREQ/PLLFLTR pin are optimized to achieve a jitter free oscillator frequency and reduced lock time.
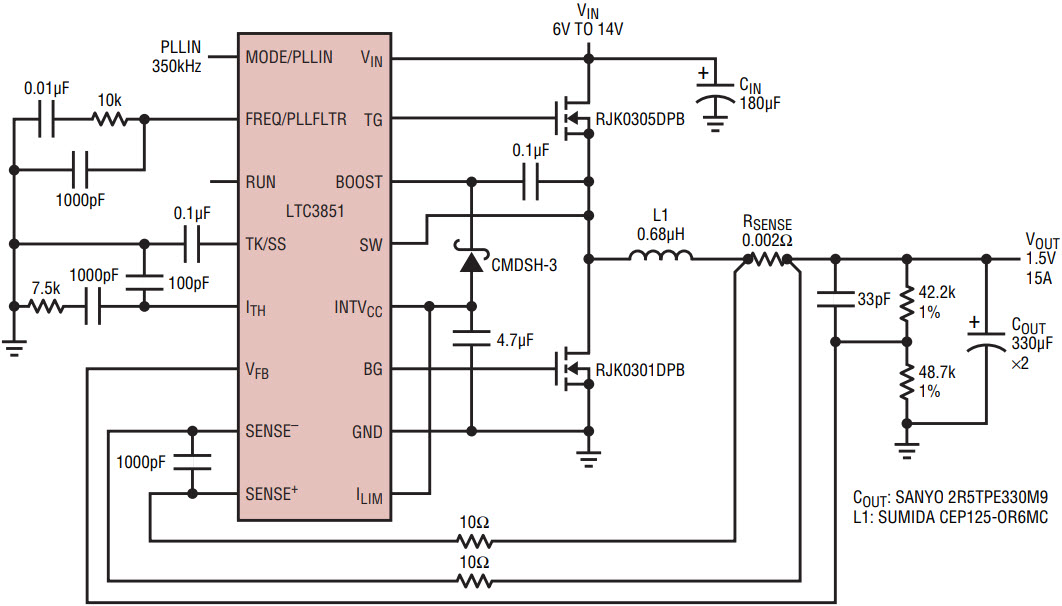
Figure 4. High efficiency 1.5V/15A power supply synchronized to 350kHz.
Conclusion
The LTC3851 combines high performance, ease of use and a comprehensive feature set in a 3mm × 3mm 16-pin package. DCR current sensing and Burst Mode® operation keep efficiency high. With a broad 4V to 38V input range, strong MOSFET drivers, low minimum on-time and tracking, the LTC3851 is ideal for automotive electronics, server farms, datacom and telecom power supply systems and industrial equipment.