Oscillator
What is an Oscillator?
定义
An electronic oscillator circuit generates an electrical signal which varies periodically in amplitude (voltage) over time such as a sine wave, square-wave, or triangle wave.
While some electronic oscillator circuits produce a signal of a fixed amplitude and frequency, in many oscillator circuits the amplitude can be increased or decreased (within design parameters) as required and the frequency of the signal can be varied (tuned). A signal generator is an example of an electronic oscillator (Figure 1).

Figure 1. Signal Generator.
How can you see a signal from an Oscillator?
The signal produced by an electronic oscillator can be viewed using a piece of equipment called an oscilloscope, which displays the signal on a screen where the y-axis represents voltage and the x-axis represents time.
Figure 2. Oscilloscope.
The length of time that elapses before a signal begins to repeat is called the wavelength (λ) and this is the inverse of its frequency (F). The relationship between frequency and wavelength is as follows:
F = 1/λ
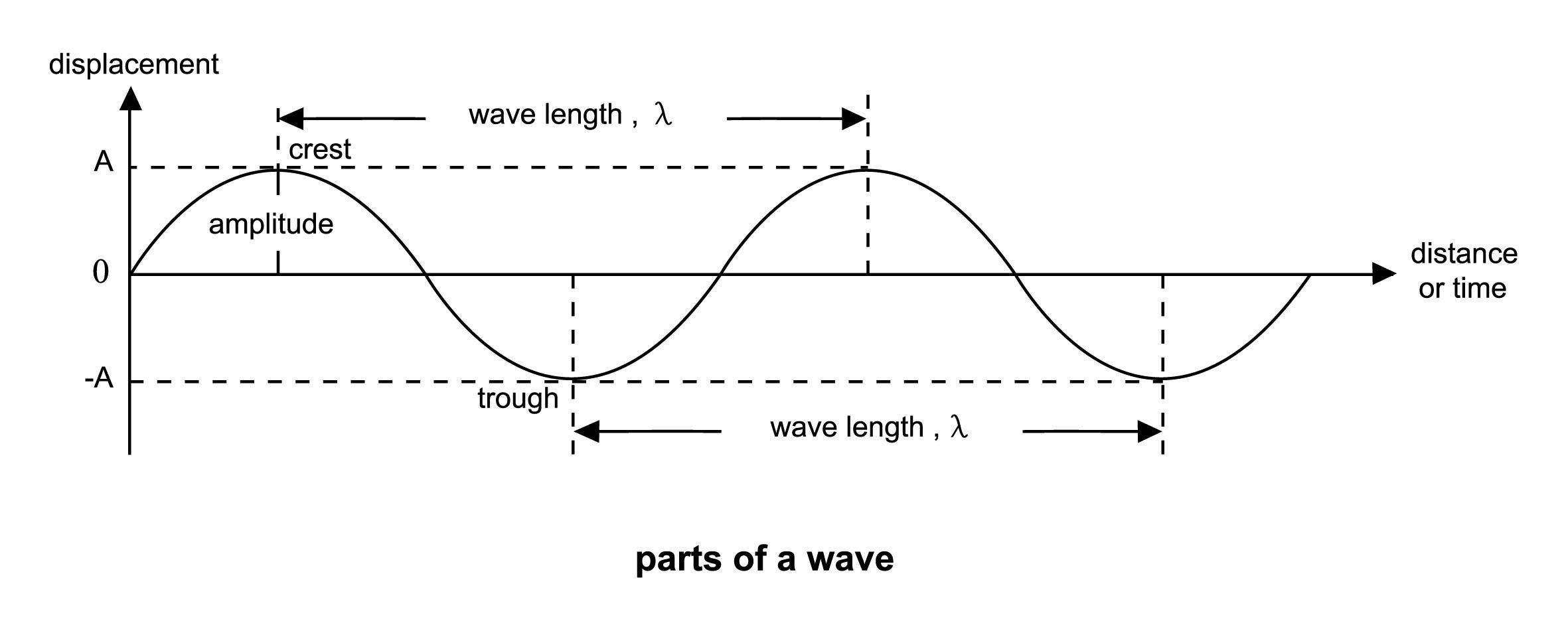
What do the terms “Amplitude” and “Wavelength” mean?
The difference between the maximum displacement and average of a signal is called the amplitude or peak voltage (Vpk).
Most modern oscilloscopes can be programmed to automatically show the voltage and frequency of the displayed signal.