48V-to-5V DC-DC Converter Using MAX638 Switching Step-Down Regulator Borrows Power from Phone Lines
Abstract
The telephone subscriber lines provide -48V voltage, but the equipment on the customer premises is usually operated from a lower voltage. The circuit using MAX638 illustrates a conversion of this available voltage to 5V required in modems, telephone test sets, and other portable systems connected to subscriber (household) telephone lines.
This circuit (Figure 1) is not battery-powered in the usual sense. Its power comes from a -48V lead-acid battery in a remote central office of the telephone system. The circuit is handy for use in modems, telephone test sets, and other portable systems connected to subscriber (household) telephone lines. It is also useful in telemetry systems.
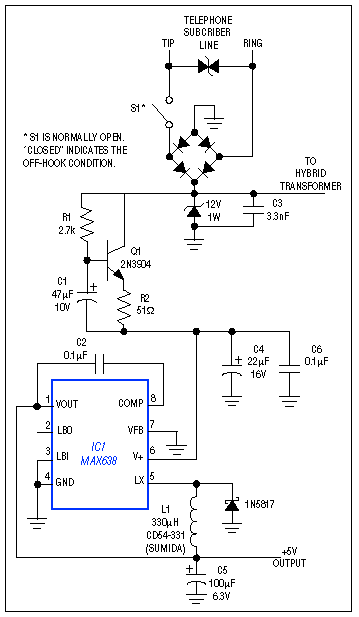
Figure 1. This circuit draws line power in the off-hook condition and delivers as much as 250mW at the 5V output, while maintaining normal voice (or data) communications over the phone lines.
For systems operating on 250mW or less, the circuit eliminates need for battery packs or ac adapters by drawing power from ordinary phone jacks. Built into peripheral equipment such as PCMCIA modem cards, the circuit can spare the main battery in a portable computer.
The current available from subscriber lines in the on-hook state is virtually zero. In the off-hook state, however, current is limited only by the sum of impedances in the central-office battery and the intervening telephone wires. Regulations such as Part 68 of the FCC rules do not restrict the current a subscriber can draw; you can even short out the line (which is what the hold button does). There is one condition: the off-hook current must exceed 20mA to ensure activation of a network-access relay in the central office.
For maximum power transfer, your impedance should match that of the line, but line impedance varies greatly, according to distance from the central office. Impedance matching is also in conflict with the need to draw at least 20mA. The 12V zener clamp, however, provides a termination that works well for line impedances up to 1700Ω. This line impedance sharply restricts the power available to you (Figure 2).
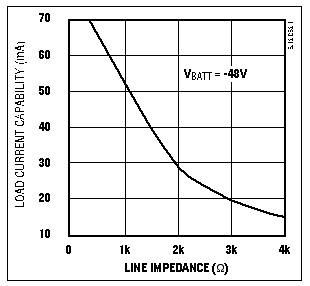
Figure 2. Available power from the Figure 1 circuit declines steeply with line impedance.
Because the circuit allows normal telephone communications while drawing power, it must block the switching noise (generated by IC1) from entering the hybrid transformer (not shown). Q1 and C1 perform this function by simulating an inductor that chokes off the noise currents. And, because the circuit sinks about 35mA regardless of the 5V load current, a "wet" hybrid transformer (one able to sink loop current) is not required. Instead, the hybrid can be a "dry" type with a smaller, lighter core.