SPIを用いてDS1390/DS1391 RTCをMotorola DSPに接続
要約
このアプリケーションノートでは、SPI™インタフェースモジュールを内蔵したMotorola DSPにDS1390を接続する方法について説明します。この回路ではMotorola DSP56F800DEMOデモボードおよびCodeWarrior®のIDEを使用します。
概要
DS1390リアルタイムクロック(RTC)は、SPIインタフェースを使用してマイクロコントローラ(µC)または Digital Signal Processing (DSP)ユニットに接続することができます。このアプリケーションノートでは、SPIインタフェースモジュールを内蔵したMotorola DSPにDS1390を接続する方法について説明します。この回路では、Motorola DSP56F800DEMOデモボードとCodeWarriorのIDEを使用します。
サンプルソフトウェアの使用
サンプルソフトウェアは、ブランクプロジェクトを出発点として開発したものです。詳細については、「Motorola Kit Installation Guide (Tutorial: Creating a CodeWarrior Project)」の指示に従ってください。このアプリケーションノートに含まれているコードをmain.cに追加してください。
動作
このプログラムは、GPIOポートを使用して、DS1390のCS信号を制御しています。ソフトウェアは、SPIコントローラモジュールを初期化し、DSPが時刻と日付をDS1390に書き込みます。次に、ソフトウェアは、時刻と日付の読み取りを繰り返します。DS1390とDS1391は、SPIモードの1と3に対応しています。
回路図を図1に示します。この回路は、ドーターカードとして構成され、Motorolaのデモボードに取り付けられます。図1の回路には、SPIインタフェースを備えた複数のRTCが搭載されています。一度に使用できるRTCは1つだけで、ソフトウェアはDS1390のみをサポートしています。ソフトウェアを図2に示します。

図1.
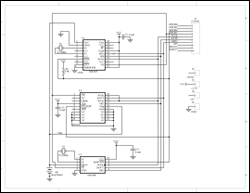
拡大画像 (PDF, 138kB)
図2. ドーターカードの回路図
図3. コードのリスト出力
/* File: DS1390.c */
/* This example program was developed using the Motorola
56F800 Demo Board Kit. Follow the kit instalation guide
for creating a CodeWarrior Project. Use the shell of the
new project for this example. Note: This program is for
example only and is not supported by Dallas Semiconductor
Maxim. */
#include "port.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
/*******************************************************
* Main program for use with Embedded SDK
*******************************************************/
extern sampleASM (void);
void reset_spi(void);
void wbyte_spi(unsigned char);
void init_sci0(Word16);
tx_sci0(unsigned char);
void bcd2ascii(unsigned char);
unsigned char rbyte_spi(void);
#define REG_BASE 0x0000
#define SCI0_BASE 0x0F00
#define SPI_BASE 0x0F20
#define GPIOA_BASE 0x0FB0
#define GPIOB_BASE 0x0FC0
#define SCI0_SCIBR *(volatile UWord16 *)(SCI0_BASE + 0)
#define SCI0_SCICR *(volatile UWord16 *)(SCI0_BASE + 1)
#define SCI0_SCISR *(volatile UWord16 *)(SCI0_BASE + 2)
#define SCI0_SCIDR *(volatile UWord16 *)(SCI0_BASE + 3)
#define SPSCR *(volatile UWord16 *)(SPI_BASE + 0)
#define SPDSR *(volatile UWord16 *)(SPI_BASE + 1)
#define SPDRR *(volatile UWord16 *)(SPI_BASE + 2)
#define SPDTR *(volatile UWord16 *)(SPI_BASE + 3)
#define GPIO_A_PUR *(volatile UWord16 *)(GPIOA_BASE + 0)
#define GPIO_A_DR *(volatile UWord16 *)(GPIOA_BASE + 1)
#define GPIO_A_DDR *(volatile UWord16 *)(GPIOA_BASE + 2)
#define GPIO_A_PER *(volatile UWord16 *)(GPIOA_BASE + 3)
#define GPIO_B_PUR *(volatile UWord16 *)(GPIOB_BASE + 0)
#define GPIO_B_DR *(volatile UWord16 *)(GPIOB_BASE + 1)
#define GPIO_B_DDR *(volatile UWord16 *)(GPIOB_BASE + 2)
#define GPIO_B_PER *(volatile UWord16 *)(GPIOB_BASE + 3)
void main (void)
{
unsigned char msec=0, min=0x26, sec=0x00, hr=0x17, dow=0x06,
date=0x26, mon=0x12, yr=0x03, write = 0;
reset_spi();
init_sci0(195); // 30MHz / 195 = 9600 baud
GPIO_B_DR = 0x0008; // disable RTC - CS high
GPIO_B_DR = 0; // enable RTC - CS low
wbyte_spi(0x8d); // control register write address
rbyte_spi(); // dummy read
wbyte_spi(0x18); // enable osc, 32kHz sqw
rbyte_spi();
GPIO_B_DR = 0x0008; // disable RTC - CS high
if(write)
{
GPIO_B_DR = 0; // enable RTC - CS low
wbyte_spi(0x80); // select seconds register write address
rbyte_spi(); // dummy read
wbyte_spi(msec); // milliseconds register data
rbyte_spi();
wbyte_spi(sec); // seconds register data
rbyte_spi();
wbyte_spi(min); // minutes register
rbyte_spi();
wbyte_spi(hr); // hours register
rbyte_spi();
wbyte_spi(dow); // day of week register
rbyte_spi();
wbyte_spi(date); // date register
rbyte_spi();
wbyte_spi(mon); // month register
rbyte_spi();
wbyte_spi(yr); // year register
rbyte_spi();
GPIO_B_DR = 0x0008; // disable RTC - CS high
}
while(1)
{
GPIO_B_DR = 0u; // enable RTC - CS low
wbyte_spi(0); // seconds register read address
rbyte_spi(); // dummy read
wbyte_spi(0);
msec = rbyte_spi(); // read milliseconds register
wbyte_spi(0);
sec = rbyte_spi(); // read seconds register
wbyte_spi(0);
min = rbyte_spi(); // ditto minutes
wbyte_spi(0);
hr = rbyte_spi(); // and so on
wbyte_spi(0);
dow = rbyte_spi();
wbyte_spi(0);
date = rbyte_spi();
wbyte_spi(0);
mon = rbyte_spi();
wbyte_spi(0);
yr = rbyte_spi();
GPIO_B_DR = 0x0008; // disable RTC - CS high
tx_sci0(0x0d); // sequence to print time & date
tx_sci0(0x0a);
bcd2ascii(yr);
tx_sci0('/');
bcd2ascii(mon);
tx_sci0('/');
bcd2ascii(date);
tx_sci0(' ');
bcd2ascii(hr);
tx_sci0(':');
bcd2ascii(min);
tx_sci0(':');
bcd2ascii(sec);
}
return;
}
//SPSCR
//15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
// r MSB SPRF ERRIE ovrf modf spte modfen spr1 spr0 sprie spmstr cpol cpha spe spite
void reset_spi()
{
int val;
SPSCR = 0x0056; // SPR0, SPMSTR, CPHA, SPE
SPDSR = 0x0007; // 8-bit size
SPSCR &= 0xfffd; // clear spe, resets SPI (partial)
SPSCR |= 0x0002; // set spe, new values take effect
GPIO_B_PER = 0x00f3; // use GPIOB3 as CS for RTC
GPIO_B_DDR = 0x000d; // direction is output
GPIO_A_PER = 0x00f9; // enable/disable per function (1=enable)
GPIO_A_DDR = 0x0006; // direction is output (1=output)
GPIO_A_DR = 0; // write bits low (0=low)
}
void wbyte_spi( unsigned char wbyte) // ------ write one byte -------
{
while (!(SPSCR & 0x0200)); // wait for transmitter empty flag
SPDTR = wbyte;
}
void bcd2ascii(unsigned char dat) // ----- convert bcd to ascii and send to sci ----
{
tx_sci0( (dat >> 4) + 0x30);
tx_sci0( (dat & 0x0f) + 0x30);
}
unsigned char rbyte_spi(void) // -------- read one byte ----------
{
while (!(SPSCR & 0x2000)); // wait for receiver full flag
return(SPDRR);
}
void init_sci0(Word16 baud)
{
GPIO_B_PER = 0x00f3; // set up
GPIO_B_DDR = 0x000d; // direction is output
SCI0_SCIBR = baud; // baud rate
SCI0_SCICR = 0x2000; // control reg
}
tx_sci0(unsigned char val)
{
UWord16 reg;
SCI0_SCICR &= 0xfffb; // turn receiver off
SCI0_SCICR |= 8; // turn transmitter on
do
{
reg = SCI0_SCISR; // clear flag by reading
} while( (reg & 0x8000) == 0); // wait until RDRF is false
SCI0_SCIDR = (unsigned int) (val);
}